Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the Modern Theory of International Trade.
Solution
Modern Theory of International Trade:
Introduction:
The modem theory of international trade was developed by Swedish economist Eli Heckscher and his student Bertil Ohlin in 1919. This model was based on the Ricardian theory of international trade. This theory says that the basis for international trade is the difference in factor endowments. It is otherwise called as ‘Factor Endowment Theory’.
The Theory:
The classical theory argued that the basis for foreign trade was comparative cost difference and it considered only labour factor. But the modem theory of international trade explains the causes for such comparative cost difference. This theory attributes international.
differences in comparative costs to:
- Difference in the endowments of factors of production between countries, and
- Differences in the factor proportions required in production.
Assumptions:
- There are two countries, two commodities, and two factors. (2 × 2 × 2 models)
- Countries differ in factor endowments.
- Commodities are categorized in terms of factor intensity.
- Countries use the same production technology.
- Countries have identical demand conditions.
- There is perfect competition in both product and factor markets in both the countries

Explanation:
According to Heckscher – Ohlin, “a capital–abundant country will export the capital–intensive goods, while the labour-abundant country will export the labour-intensive goods”. A factor is regarded as abundant or scarce in relation to the quantum of other factors. A country can be regarded as richly endowed with capital only if the ratio of capital to other factors is higher than other countries
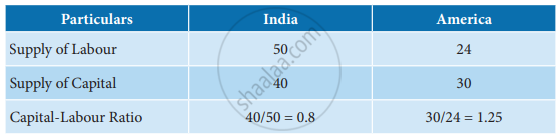
In the above example, even though India has more capital in absolute terms, America is more richly endowed with capital because the ratio of capital in India is 0.8 which is less than that in America where it is 1.25. The following diagram illustrates the pattern of world trade.

Limitations:
- Factor endowment of a country may change over time.
- The efficiency of the same factor (say labour) may differ in the two countries. For example, America may be labour scarce in terms of the number of workers. But in terms of efficiency, the total labour may be larger.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In general, a primary reason why nations conduct international trade is that ______.
Which of the following is a modern theory of international trade?
Net export equals ______.
What is the main difference between Adam Smith and Ricardo with regard to the emergence of foreign trade?
Compare the Classical Theory of international trade with the Modern Theory of International trade.
Explain briefly the Comparative Cost Theory.
