Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the role of hybridisation in crop improvement.
Solution
The crossing between genetically dissimilar plants to produce a new kind (hybrid) is called hybridisation. Crossing may be between two different varieties (intervarietal), between two different species (interspecific) and between different genera (intergeneric).
Cross-breeding of two varieties of plants is carried out to obtain an improved variety of plants which will combine in it both the desired characteristics of parent crop plants. For example, the new improved variety of crop plants, thus obtained will give a high yield of food grains and it will be disease resistant too. This process of cross-breeding of different plants to obtain a new improved variety of crops is called hybridisation.
Selection and hybridisation are often combined inbreeding. In India, crops are grown in diverse types of soil and different climatic conditions by poor to progressive farmers. Keeping in mind climatic factors, input application, disease and pest resistance, quality and adaptability etc. a large number of varieties have been developed by hybridisation. Such varieties are high-yielding, resistant to diseases and pests, have better quality and early to late maturing time.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Weeds affect the crop plants by
Berseem is an important ______ crop.
______ are rich in vitamins.
______ crop grows in winter season.
What is a GM crop? Name anyone such crop which is grown in India.
Kharif crops are cultivated from ______ to ______.
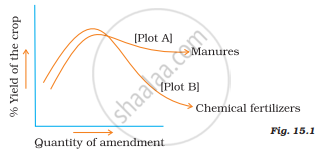
Figure15.1 shows the two crop fields [Plots A and B] have been treated by manures and chemical fertilizers respectively, keeping other environmental factors the same. Observe the graph and answer the following questions.
(i) Why does plot B show a sudden increase and then a gradual decrease in yield?
(ii) Why is the highest peak in plot A graph slightly delayed?
(ii) What is the reason for the different patterns of the two graphs?