Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Distinguish between action spectrum and absorption spectrum.
Solution
| Action Spectrum | Absorption Spectrum | |
| 1. | The curve that shows the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths is called action spectrum. | The curve which shows the amount of light absorbed by pigments at each wavelength is termed as absorption spectrum |
| 2. | It explains the relationship between photosynthetic activity in relation to different wavelengths of light. | It explains the relationship between quality of light and absorbing capacity of the pigments. |
| 3. | In action spectrum, the rate of photosynthesis is measured as amount of CO2 fixation, oxygen production, NADP+ reduction. | In absorption spectrum, absorption of different wavelengths of light pigments can be measured by spectrophotometer. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Solve Numerical example.
A monochromatic ray of light strike the water (n = 4/3) surface in a cylindrical vessel at angle of incidence 53°. Depth of water is 36 cm. After striking the water surface, how long will the light take to reach the bottom of the vessel? [Angles of the most popular Pythagorean triangle of sides in the ratio 3:4:5 are nearly 37°, 53°, and 90°]
Answer the following question.
What is the advantage of having more than one pigment molecule in a photocenter?
Answer the following question.
Why is photolysis of water accompanied with non-cyclic photophosphorylation?
Light of wavelength 5000 A.U. falls on a plane reflecting surface. The frequency of reflected light is ______
Which of the following is not a property of light?
A ray of light is incident at an angle ion one face of prism of small angle A and emerges normally from the other surface. µ is the refractive index of the material of the prism. The angle of incidence is _____________.
In the biprism experiment, fringes are obtained using monochromatic light. The distance between the 5th bright band and 9th dark band on the same side of the central bright band, in terms of the fringe width 'X' is ______
The critical angle for light travelling from medium P to medium Q is 'θ'. The speed of light in medium P is 'v'. Then the speed of light in medium Q is ______.
In a compound microscope, let u0 and v0 be the object distance and image distance respectively. The objective of focal length f0 magnifies a tiny object into a real, inverted image. The linear magnification of the objective is ______.
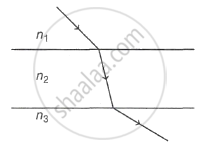
A beam of light passes from medium 1 to medium 2 to medium 3 as shown in the diagram. What may be concluded about the three refractive indices n1, n2 and n3?