Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Distinguish between uniform velocity and variable velocity.
Solution
| Uniform velocity | Variable velocity |
| If a body travels equal distances in equal intervals of time along a particular direction, then the body is said to be moving with a uniform velocity. | If a body travels unequal distances in a particular direction in equal intervals of time or it moves equal distances in equal intervals of time but its direction of motion does not remain same, then the velocity of the body is said to be variable (or non-uniform). |
| Example - A body, once started on a frictionless surface, moves with uniform velocity. | Example - The motion of a body in circular path, even with uniform speed is with variable velocity as the direction of motion of body continuously changes with time. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Observe the figure and answer the questions.
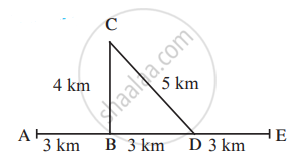
Sachin and Sameer started on a motorbike from place A, took the turn at B, did a task at C, travelled by the route CD to D and then went on to E. Altogether, they took one hour for this journey.
Find out the actual distance traversed by them and the displacement from A to E. From this, deduce their speed.
What was their velocity from A to E in the direction AE?
Can this velocity be called average velocity?
A body goes from P to Q with a uniform speed of u and immediately returns back to P at a uniform speed of v. what is the average velocity for the whole journey?
When a body said to have a uniform velocity?
A circular cycle track has a circumstance of 314 m with AB as one of its diameter. A cyclist travels from A to B along the circular path with a velocity of constant magnitude 15. 7 m/ s. Find :
(a) The distance moved by the cyclist.
(b) The displacement of the cyclist if AB represents north-south direction .
(c) The average velocity of the cyclist.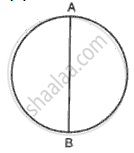
Figure represents graphically the velocity of a car moving along a straight road over a period of 100 hours.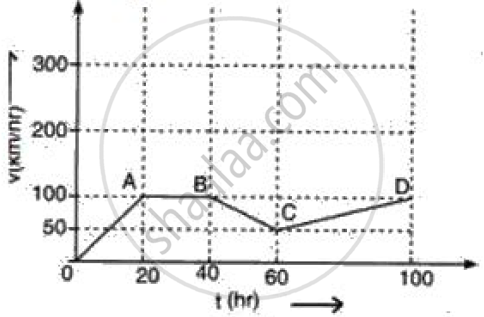
How long is the body travelling with a uniform velocity?
A body moves with an initial velocity of 5ms-1 and accelerates at 2ms -2. Its velocity after 10s is ______.
Assertion: A body can have acceleration even if its velocity is zero at a given instant of time.
Reason: A body is momentarily at rest when it reverses its direction of motion.
Define velocity.
Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Distinguish between speed and velocity.
