Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Draw a diagram of the microscopic structure of human sperm. Label the following parts in it and write their functions
(a) Acrosome
(b) Nucleus
(c) Middle piece
Draw a diagram of a mature human sperm. Label any three parts and write their functions.
Explain the structure of human sperm with labelled diagram.
Solution 1
Structure of human sperm

Function of Acrosome-It releases various chemicals like hyaluronidase and acrosin which helps sperm in fusing with egg cell.
Function of Nucleus-It stores the genetic information. It carries 23 chromosomes, out of which one is sex chromosome (either X or Y). Thus, it is responsible for determining the sex of the individual.
Function of Middle piece-The middle piece contains several mitochondria, which produce energy for the motility of the sperm.
Solution 2

- Head: It the flat oval part of the human sperm that contains the nucleus, containing genetic material, and acrosome, a small anterior part which is formed from Golgi complex. It secretes hyaluronidase enzyme which helps in the entry of sperm into the egg.
- Middle Piece: It is the middle, cylindrical portion of the sperm, which contains numerous mitochondria. They provide energy (ATP) to the sperm for its movement.
- Tail: It is the long, tapering structure composed of cytoplasm. It helps in the movement of the sperms inside the uterus.
Solution 3

Sperm is the male gamete. It is a motile, microscopic and elongated cell. The sperm is divisible into three parts: Head, middle piece, and tail.
- Head: The sperm head is oval in shape and contains haploid nucleus. Above the nucleus, there is a cap like structure called acrosome which is formed from the Golgi body. Acrosome contains hydrolytic enzymes like hyaluronidase and proteolytic enzymes like zona lysins and corona penetrating enzymes.
- Neck: It is a very short region having two centrioles i.e. proximal centriole and distal centriole.
- Middle piece: It has an axial filament surrounded by 10-14 spiral turns of mitochondria (Nebenkern). It produces energy necessary for the movement of sperm.
- Tail: It is a long, slender, and tapering part containing cytoplasm and fine thread i.e. axial filament. The axial filament arises from the distal centriole and travels throughout the length of tail. It is partly surrounded by plasma membrane (main piece). The part without plasma membrane is called end piece.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe the process of budding in hydra.
Fill in the blank.
Implantation of embryo occurs in ------
In case of sexual reproduction, newborn show similarities about characters. Explain this statement with suitable examples.
If newborns are produced at the age of menopause, they may be with some abnormalities. Why?
The process which the sperm undergoes before penetrating the ovum is ____________.
Answer the following type of question Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
(A) - Head of the sperm consists of acrosome and mitochondria.
(R) - Acrosome contains spiral rows of mitochondria.
Expand the acronym.
LH
During spermatogenesis, spermatogonium grows in size to become ______.
Formation of ____________ is an indication of the termination of oogenesis.
500 spermatozoa are formed from ____________ secondary spermatocytes.
Identify the correct stages (P - S) in the given diagram of spermatogenesis.
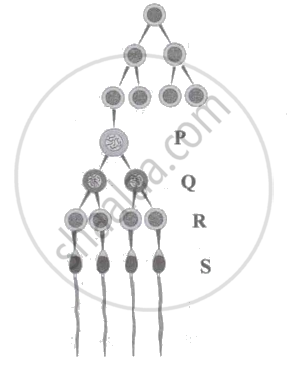
In oogenesis haploid egg is fertilised by sperm at which stage?
Which of the following are called dual gland?
Fetal sex can be determined by examining cells from amniotic fluid looking for:
Growth hormone of pituitary is more effective in ______.
In spermatogenesis, at the end of the first meiotic division ______ are formed.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of spermatogenesis.
Answer the following:
How many primary spermatocytes and oocytes are required for the formation of 100 spermatozoa and ova?
Explain Oogenesis with diagram.
Distinguish between human sperm and ovum.
