Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Solution
Diagram for a refracted ray of light:
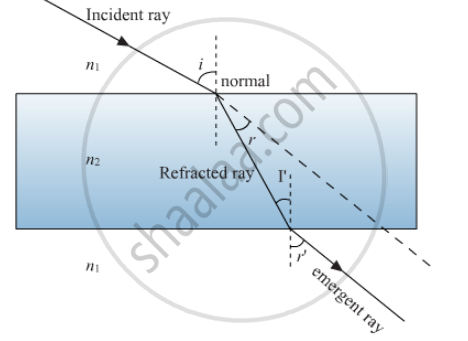
Here,
i = Angle of incidence
r = Angle of refraction
i' = Angle of incident at the emergent point
r' = Angle of refraction at the emergent point
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
State any two uses of convex lenses.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
Observe the following figure and complete the table:

| Points | Answer |
| (i) Position of the object | |
| (ii) Position of the image | |
| (iii) Size of the image | |
| (iv) Nature of the image |
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
