Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
Solution
(a)
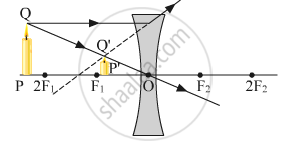
(b) The object distance (u) and the image distance (v) are indicated in the figure given below.
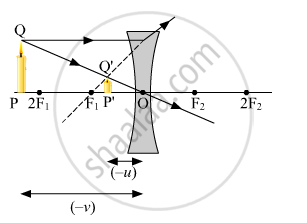
Since both the image and the object lie in the direction opposite to the direction of the incoming ray, both will be negative. The relation between u, v and f given by the lens formula is
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
As both u and v are negative, the above equation will be changed to
`1/f=1/((-v))-1/((-u))`
`1/f=-1/v+1/u`
`1/f=1/u-1/v`
We know that the focal length of a concave lens is negative. Using the same argument, the above equation will be changed to
`1/-f=1/u-1/v`
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
(c) Given:-
u = −40 cm
m = −1
Since magnification is given as
`m=v/u`
`rArrv="mu "=(-1)xx(-40)=40" cm"`
Focal length can be calculated as
`1/f=1/v-1/u=1/40-1/((-40))=1/20`
`rArrf=20" cm"`
Now, the power of the convex lens can be calculated as
`P=1/f(m)=100/20="5 D"`
Since the power of the lens is positive, the lens will be converging in nature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
Complete the following table:
| Instrument | Number of Convex Lenses |
Use |
| Simple Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Compound Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Telescope | .............. | .............. |
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from an optically denser medium into air.
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: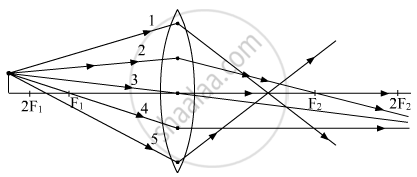
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
The image obtained while finding the focal length of convex lens is ....................
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
We can burn a piece of paper by focussing the sun rays by using a particular type of lens. Name the type of lens used for the above purpose. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
