Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
उत्तर
(a)
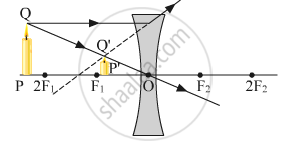
(b) The object distance (u) and the image distance (v) are indicated in the figure given below.
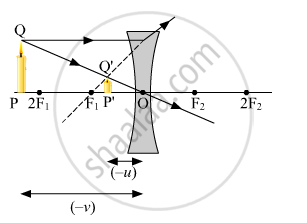
Since both the image and the object lie in the direction opposite to the direction of the incoming ray, both will be negative. The relation between u, v and f given by the lens formula is
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
As both u and v are negative, the above equation will be changed to
`1/f=1/((-v))-1/((-u))`
`1/f=-1/v+1/u`
`1/f=1/u-1/v`
We know that the focal length of a concave lens is negative. Using the same argument, the above equation will be changed to
`1/-f=1/u-1/v`
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
(c) Given:-
u = −40 cm
m = −1
Since magnification is given as
`m=v/u`
`rArrv="mu "=(-1)xx(-40)=40" cm"`
Focal length can be calculated as
`1/f=1/v-1/u=1/40-1/((-40))=1/20`
`rArrf=20" cm"`
Now, the power of the convex lens can be calculated as
`P=1/f(m)=100/20="5 D"`
Since the power of the lens is positive, the lens will be converging in nature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block).
State any two uses of convex lenses.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
Out of the two lenses one concave and the other convex state which is a convergent or a divergent type of a lens. Give a reason for your answer.
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
