Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
उत्तर
- Convex lens
- `1/f = 1/v - 1/u`
In this case, v = 7m and f = 5m
Putting the values in the equation, we get,
`1/5 = 1/7 - 1/u`
`1/u = 1/7 - 1/5 = (5 - 7)/35 = (-2)/35`
`u = -35/2 = -17.5` m
The object will be placed 17.5 m on the left of the convex lens. 
(two rays, arrows, and object placed beyond 2f on the left)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The image in a convex lens depends upon the distance of the ........... from the lens.
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
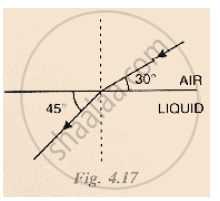
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
Study the diagram below.
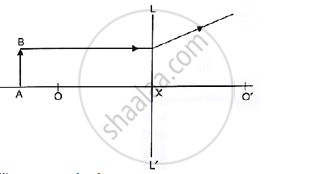
what are the points O, O’ called?
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
To find the image distance for varying object distances in case of a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object by placing it at 20 cm distance from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object away from the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) How does the size of image change?
(c) Approximately at what distance does he obtain the image of magnification –1?
(d) How does the intensity of image change as the object moves farther and farther away from the lens?
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
How will you decide whether a given piece of glass is a concave lens, convex lens, or a plane glass plate?
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
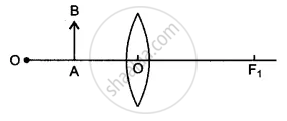
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
