Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
Options
5
10
20
60
Solution
20 times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
A ray of light travelling in water emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
A 1 cm high object is placed at a distance of 2f from a convex lens. What is the height of the image formed?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
A burning candle whose flame is 1.5 cm tall is placed at a certain distance in front of a convex lens. An image of candle flame is received on a white screen kept behind the lens. The image of flame also measures 1.5 cm. If f is the focal length of convex lens, the candle is placed:
(a) at f
(b) between f and 2f
(c) at 2f
(d) beyond 2f
What is the position of image when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm?
Describe the nature of image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
A camera fitted with a lens of focal length 50 mm is being used to photograph a flower that is 5 cm in diameter. The flower is placed 20 cm in front of the camera lens.
At what distance from the film should the lens be adjusted to obtain a sharp image of the flower?
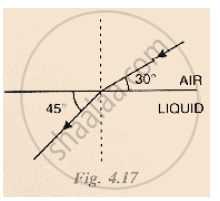
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens
. 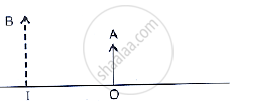
draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –60 | +12 |
| 2 | –30 | +15 |
| 3 | –20 | +20 |
| 4 | –15 | +30 |
| 5 | –12 | +60 |
| 6 | –9 | +90 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? State reason for your answer.
(b) For what object-distance (u) is the corresponding image-distance (v) not correct? How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Choose an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
To find the image distance for varying object distances in case of a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object by placing it at 20 cm distance from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object away from the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) How does the size of image change?
(c) Approximately at what distance does he obtain the image of magnification –1?
(d) How does the intensity of image change as the object moves farther and farther away from the lens?
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
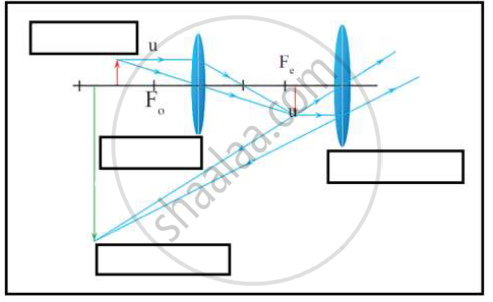
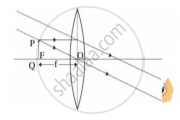
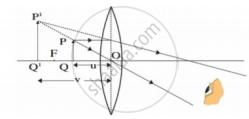
i. Which type of microscope has the arrangement of lenses shown in the adjoining figure?
ii. Label the figure correctly.
iii. Write the working of this microscope.
iv. Where does this microscope used?
v. Suggest a way to increase the efficiency of this microscope.
The image obtained while finding the focal length of convex lens is ....................
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ :