Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
Solution
u = -15 cm
f = 20
Substituting these values in the lens formula, we get:
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
`1/20=1/v-1/-15`
`1/20=1/v+1/15`
`1/20-1/15=1/v`
`1/v=(3-4)/60`
`1/v=-1/60`
v=-60 cm
The image will be formed at a distance of 60 cm in front of the mirror.
`m=v/u`
⇒`m=(- 60)/-15`
⇒m=4
Magnification is positive; therefore, the image is virtual and
erect.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
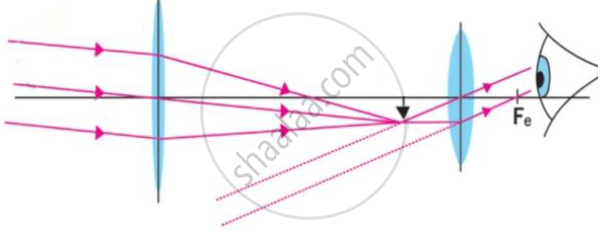
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
Draw a diagram to show the convergent action of a convex lens by treating it as a combination of glass block and two triangular glass prisms, with the aid of two parallel incident rays.
