Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
Options
power 2 D; convex lens
power 1 D; concave lens
power - 0.5 D; concave lens
power - 0.25 D; convex lens
Solution
power 2 D; convex lens
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
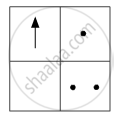
(a)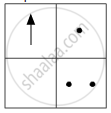
(b)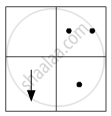
(c)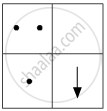
(d)
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
Complete the following table:
| Instrument | Number of Convex Lenses |
Use |
| Simple Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Compound Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Telescope | .............. | .............. |
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. The focal length of this combination of lenses will be:
(a) +10 cm
(b) +20 cm
(c) −10 cm
(d) −20 cm
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
Study the diagram given below.
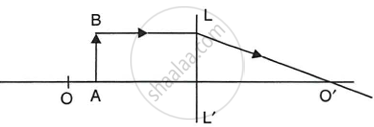
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O’ called?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State the three characteristics of the image.
- Name a device in which this action of lens is used.
Study the diagram below.
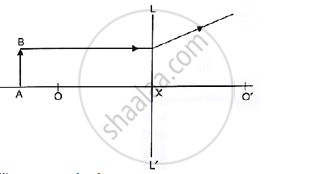
what are the points O, O’ called?
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
A lens forms an inverted image of an object. Name the kind of lens.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
Observe the following figure and complete the table:

| Points | Answer |
| (i) Position of the object | |
| (ii) Position of the image | |
| (iii) Size of the image | |
| (iv) Nature of the image |
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
The focal length of a lens is positive. In this case, state the kind of lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of astronomical telescope.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
A concave mirror and convex lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal length?
Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object?
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
Which of the following statements is true?
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
