Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
Solution
Object distance, u = – 20 cm
Object height, h = 5 cm
Radius of curvature, R = 30 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 × Focal length
R = 2f
f = `30/2`
f = 15 cm
According to the mirror formula,
`1/"f" = 1/"v" + 1/"u"`
`1/15 = 1/"v" + 1/(-20)`
`1/15 = 1/"v" - 1/20`
`1/15 + 1/20 = 1/"v"`
`1/"v" = (4 + 3)/60`
`1/"v" = 7/60`
v = `60/7`
v = 8.57 cm
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.
The positive value of magnification indicates that the image formed is virtual.
Size of the image:
m = `"h'"/"h" = -"v"/"u"`
`"h'"/5 = (-8.57)/(-20)`
20 h' = 8.57 × 5
20 h' = 42.9
h' = `42.85/20`
h' = 2.14 cm
The positive value of image height indicates that the image formed is erect.
Therefore, the image formed is virtual, erect, and smaller in size.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
A teacher sets up the stand carrying a convex lens of focal length 15 cm at 42.7 cm mark on the optical bench. He asks four students A, B, C and D to suggest the position of screen on the optical bench so that a distinct image of a distant tree is obtained almost immediately on it. The positions suggested by the students were as
A. 12.7 cm
B. 29.7 cm
C. 57.7 cm
D. 72.7 cm
The correct position of the screen was suggested by
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: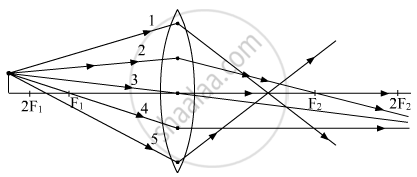
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
Out of the two lenses one concave and the other convex state which is a convergent or a divergent type of a lens. Give a reason for your answer.
Write the name.
The lens used in simple microscope.
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
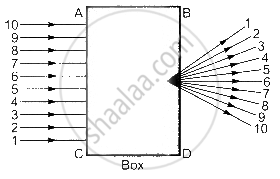
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
