Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
उत्तर
Object distance, u = – 20 cm
Object height, h = 5 cm
Radius of curvature, R = 30 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 × Focal length
R = 2f
f = `30/2`
f = 15 cm
According to the mirror formula,
`1/"f" = 1/"v" + 1/"u"`
`1/15 = 1/"v" + 1/(-20)`
`1/15 = 1/"v" - 1/20`
`1/15 + 1/20 = 1/"v"`
`1/"v" = (4 + 3)/60`
`1/"v" = 7/60`
v = `60/7`
v = 8.57 cm
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.
The positive value of magnification indicates that the image formed is virtual.
Size of the image:
m = `"h'"/"h" = -"v"/"u"`
`"h'"/5 = (-8.57)/(-20)`
20 h' = 8.57 × 5
20 h' = 42.9
h' = `42.85/20`
h' = 2.14 cm
The positive value of image height indicates that the image formed is erect.
Therefore, the image formed is virtual, erect, and smaller in size.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
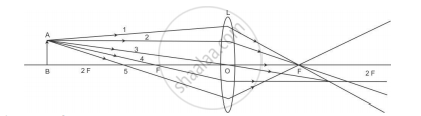
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Describe the nature of image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
To find the image distance for varying object distances in case of a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object by placing it at 20 cm distance from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object away from the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) How does the size of image change?
(c) Approximately at what distance does he obtain the image of magnification –1?
(d) How does the intensity of image change as the object moves farther and farther away from the lens?
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: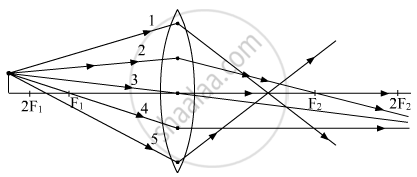
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find (i) the position (ii) the magnification and (iii) the nature of the image formed.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
Convex lens is also known as ______.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
