Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
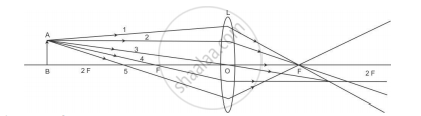
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
उत्तर
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Ray 2, 3 and 4 are obeying the laws of refraction.
Ray 2 is parallel to the principal axis and passes through the principal focus after refraction.
Ray 3 passes from the optical centre of the lens and emerges without any deviation.
Ray 4 is passing through the principal focus and after refraction from a convex lens emerges parallel to the principal axis.
Ray 1 and 5 cannot pass through the focus after refraction as they are not parallel to the principal axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.50 m
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
Where is the image formed?
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
