Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
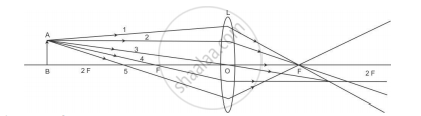
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Solution
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Ray 2, 3 and 4 are obeying the laws of refraction.
Ray 2 is parallel to the principal axis and passes through the principal focus after refraction.
Ray 3 passes from the optical centre of the lens and emerges without any deviation.
Ray 4 is passing through the principal focus and after refraction from a convex lens emerges parallel to the principal axis.
Ray 1 and 5 cannot pass through the focus after refraction as they are not parallel to the principal axis.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
Where is the image formed?
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
