Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
Solution
Image formation diagram:
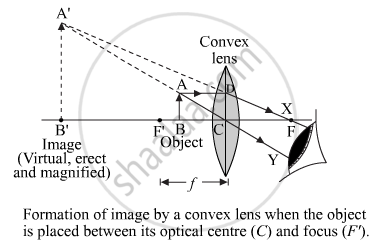
Characteristics of the image so formed:
1) On the same side as that of the object or behind the lens
2) Nature of image – virtual and erect
3) Size of Image – enlarged
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Complete the following sentence.
A long-sighted person cannot see ........... objects clearly. Long-sightedness can be corrected by using .............. lenses.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens
. 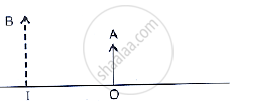
draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus.
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
