Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Options
Simple microscope
Compound microscope
Telescope
Prism
Solution
Prism
Explanation-
Prism disperses light while other optical instruments produce magnified images of objects.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –100 | +25 |
| 2 | –60 | +30 |
| 3 | –40 | +40 |
| 4 | –30 | +60 |
| 5 | –25 | +100 |
| 6 | –15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
A beam of light travelling in air is incident of water. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in water.
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass?
For what position of an object a real, diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
What is a lens?
Define principal axis, principal focus and focal length of a convex lens.
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
What kind of lens can form:
am erect diminished image?
A camera fitted with a lens of focal length 50 mm is being used to photograph a flower that is 5 cm in diameter. The flower is placed 20 cm in front of the camera lens.
At what distance from the film should the lens be adjusted to obtain a sharp image of the flower?
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is:
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ______.
The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object?
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
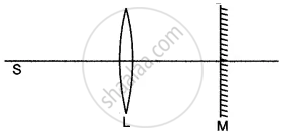
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
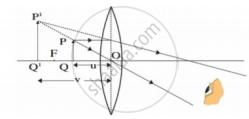
A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
How will you determine the focal length of a convex lens by the plane mirror method?
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 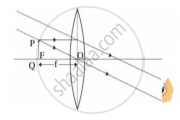
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
