Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
विकल्प
Simple microscope
Compound microscope
Telescope
Prism
उत्तर
Prism
Explanation-
Prism disperses light while other optical instruments produce magnified images of objects.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
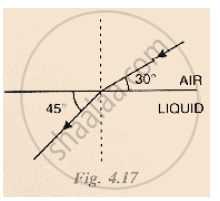
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
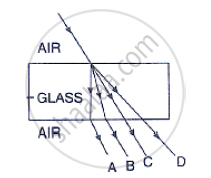
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is:
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is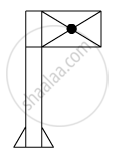
(A)
(B)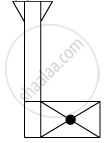
(C)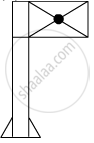
(D)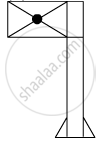
While determining the focal length of a convex lens, you try to focus the image of a distant object formed by the lens on the screen. The image formed on the screen, as compared to the object, should be
(A) erect and highly diminished
(B) erect and enlarged
(C) inverted and enlarged
(D) inverted and highly diminished
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.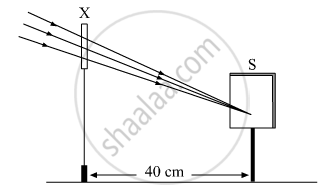
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
List four properties of the image formed by a convex mirror.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
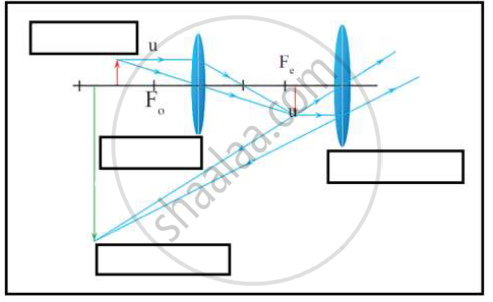
i. Which type of microscope has the arrangement of lenses shown in the adjoining figure?
ii. Label the figure correctly.
iii. Write the working of this microscope.
iv. Where does this microscope used?
v. Suggest a way to increase the efficiency of this microscope.
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
State two applications of a convex lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in observing biological specimens.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a virtual and magnified image.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
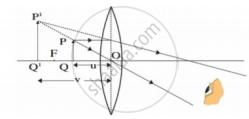 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 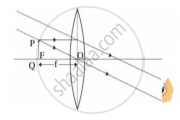
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
Convex lens is also known as ______.
