Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
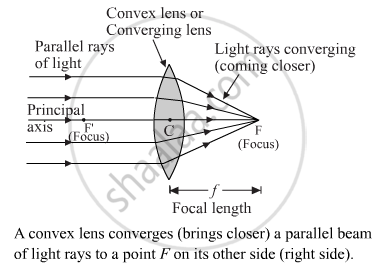
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
उत्तर
Suppose that a parallel beam of light rays falls on a convex lens as shown in the figure. These light rays are parallel to one another and also to the axis of the lens. The incident rays pass through the convex lens and get refracted according to the laws of refraction. All the rays, after passing through the convex lens, converge at the same point F, on the other side of the lens. The point F is called the principal focus of the convex lens. Thus, the point of convergence of the parallel beam of light rays to a single point is called the focus of the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
State any two uses of convex lenses.
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
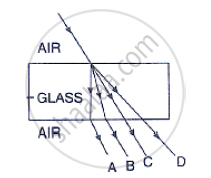
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
Write the name.
The lens used in simple microscope.
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
