Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
उत्तर
Ray diagram:

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens.
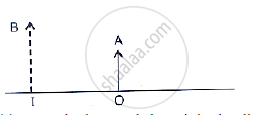
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: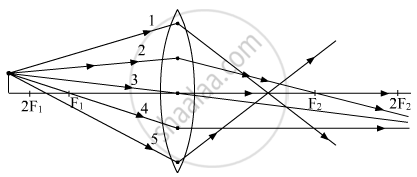
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
Can a normal convex lens behave like a concave lens and vice-versa?
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
