Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
उत्तर
In sunglasses, the outer surface is convex and the inner surface is concave, hence the power of one surface is positive and that of the other is negative. By making both these powers equal, the effective power of the lens becomes zero. Hence, these lenses are simply like a thin glass having no power, plus or minus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
A ray of light travelling in water emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
You eye contains a convex lens. Why is it unwise to look at the sun?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
Study the diagram below.
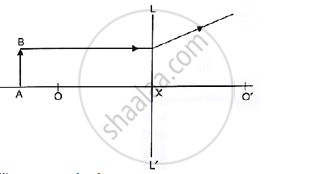
what are the points O, O’ called?
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

