Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
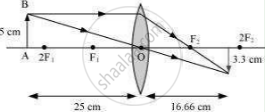
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
उत्तर १
Given:
Object distance, u = −25 cm
Object height, ho = 5 cm
Focal length, f = +10 cm
According to the lens formula,
`1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
`1/v = 1/f + 1/u = 1/10 - 1/25 = 15/250`
`v=250/15=16.66` cm
The positive value of v shows that the image is formed at the other side of the lens.
Magnification m =`-"image distance"/"object distance"=-v/u = 16.66/25 = -0.66`
The negative sign shows that the image is real and formed behind the lens.
Magnification m =`"image height"/"object height" = "H"_i/"H"_o = "H"_i/5`
Hi = m × Ho= −0.66 × 5 = −3.3 cm
The negative value of the image height indicates that the image is inverted. The position, size, and nature of image are shown in the following ray diagram.
उत्तर २
Given:
Object distance, u = −25 cm
Focal length, f = 10 cm
Height of the object, h = 5 cm
Applying the lens formula, we get:
`1/f = 1/v - 1/u`
⇒`1/v = 1/f + 1/u`
⇒`1/v = 1/f + 1/u`
⇒`11/2/v = 1/10 + 1/-25`
⇒`1/v = (5 - 2)/50`
⇒ `1/v = 3/50`
⇒ v = `50/3`
⇒ v = 16.67 cm
The image will be at a distance of v cm behind the lens.
m = `"h'"/"h" = "v"/"u"`
⇒ `"h'"/5 = (50/3)/(-25)`
⇒ `"h'"/5 = 50/(3 xx -25)`
⇒ `"h'"/5 = 2/(-3)`
⇒ −3h' = 5 × 2
⇒ −3h' = 10
⇒ h' = `10/(-3)`
⇒ h' = – 3.33 cm
Size of the image: The image is smaller than the object. And the negative sign indicates that the image is real and inverted.
Nature of image: Real and inverted.
Ray diagram:

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass?
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
A lens forms an inverted image of an object. Name the kind of lens.
A teacher sets up the stand carrying a convex lens of focal length 15 cm at 42.7 cm mark on the optical bench. He asks four students A, B, C and D to suggest the position of screen on the optical bench so that a distinct image of a distant tree is obtained almost immediately on it. The positions suggested by the students were as
A. 12.7 cm
B. 29.7 cm
C. 57.7 cm
D. 72.7 cm
The correct position of the screen was suggested by
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.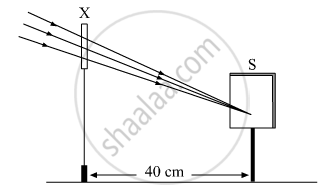
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used in cine projector.
Write the three characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens of focal length 20 cm for the object at distance (i) 10 cm, (ii) 30 cm, (iii) 40 cm, (iv) 60 cm from the lens.
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
Which of the following statements is true?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
