Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
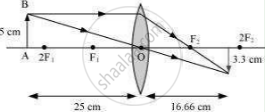
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Solution 1
Given:
Object distance, u = −25 cm
Object height, ho = 5 cm
Focal length, f = +10 cm
According to the lens formula,
`1/v - 1/u = 1/f`
`1/v = 1/f + 1/u = 1/10 - 1/25 = 15/250`
`v=250/15=16.66` cm
The positive value of v shows that the image is formed at the other side of the lens.
Magnification m =`-"image distance"/"object distance"=-v/u = 16.66/25 = -0.66`
The negative sign shows that the image is real and formed behind the lens.
Magnification m =`"image height"/"object height" = "H"_i/"H"_o = "H"_i/5`
Hi = m × Ho= −0.66 × 5 = −3.3 cm
The negative value of the image height indicates that the image is inverted. The position, size, and nature of image are shown in the following ray diagram.
Solution 2
Given:
Object distance, u = −25 cm
Focal length, f = 10 cm
Height of the object, h = 5 cm
Applying the lens formula, we get:
`1/f = 1/v - 1/u`
⇒`1/v = 1/f + 1/u`
⇒`1/v = 1/f + 1/u`
⇒`11/2/v = 1/10 + 1/-25`
⇒`1/v = (5 - 2)/50`
⇒ `1/v = 3/50`
⇒ v = `50/3`
⇒ v = 16.67 cm
The image will be at a distance of v cm behind the lens.
m = `"h'"/"h" = "v"/"u"`
⇒ `"h'"/5 = (50/3)/(-25)`
⇒ `"h'"/5 = 50/(3 xx -25)`
⇒ `"h'"/5 = 2/(-3)`
⇒ −3h' = 5 × 2
⇒ −3h' = 10
⇒ h' = `10/(-3)`
⇒ h' = – 3.33 cm
Size of the image: The image is smaller than the object. And the negative sign indicates that the image is real and inverted.
Nature of image: Real and inverted.
Ray diagram:

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
List some things that convex lens and concave mirror have in common.
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
Study the diagram below.
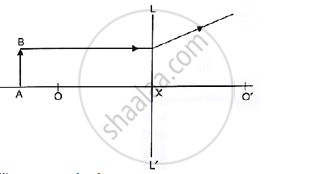
what are the points O, O’ called?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
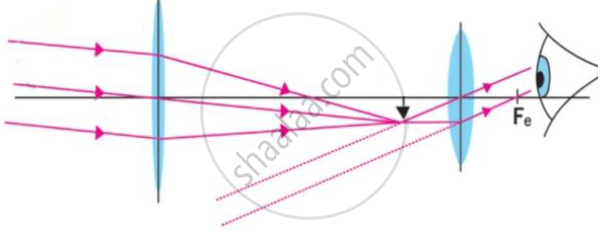
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

We can burn a piece of paper by focussing the sun rays by using a particular type of lens. Name the type of lens used for the above purpose. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
