Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
Options
simple microscope
compound microscope
telescope
none of these
Solution
Compound microscope is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
"A lens can form a magnified erect image as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." State the nature of this lens and draw ray diagrams to justify the above statement. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in the diagram.
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block).
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its real, inverted and magnified image?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ........
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
What kind of lens is used to correct
long-sightedness?
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ______.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
Answer the following question.
List four precautions which a student should observe while determining the focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining an image of a distant object on a screen.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
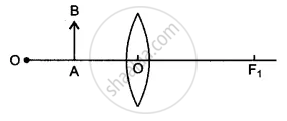
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Convex lens is also known as ______.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
