Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block).
Solution
If it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block):

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the concave lens in the case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 at a distance of 40 cm from the optical centre.
For what position of an object a real, diminished image is formed by a convex lens?
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: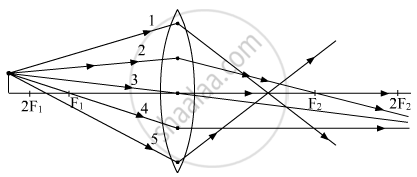
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of astronomical telescope.
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
