Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block).
उत्तर
If it hits the glass block at an angle other than 90° (that is, obliquely to the glass block):

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
An image formed on a screen is three times the size of the object. The object and screen are 80 cm apart when the image is sharply focussed.
State which type of lens is used.
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens
. 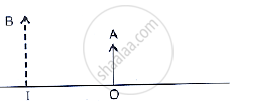
draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
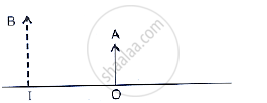
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –60 | +12 |
| 2 | –30 | +15 |
| 3 | –20 | +20 |
| 4 | –15 | +30 |
| 5 | –12 | +60 |
| 6 | –9 | +90 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? State reason for your answer.
(b) For what object-distance (u) is the corresponding image-distance (v) not correct? How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Choose an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
A pin 2 cm long is placed 12 cm away from a convex lens at right angles to the principal axis. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, by scale drawing find the size of the image and its magnification.
A concave mirror and convex lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal length?
