Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain why, a stick half immersed in water appears to be bent at the surface. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
Solution
When a stick is half immersed in water, it appears to be bent at the surface due to the refraction of light.
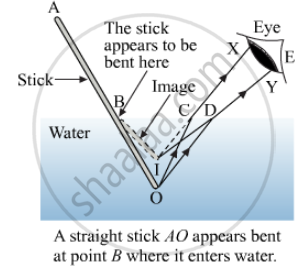
In the above figure, the half portion BO of stick AO is immersed in water and it appears to be bent at point B. The light ray OC coming from the lower end O of the stick passes from water to air and gets refracted away from the normal in the direction CX. Another ray OD is refracted in the direction DY. These two refracted rays, i.e, CX and DY meet at point I, when produced backwards. The point I is nearer to the water surface than point O. Therefore, a virtual image of end O of the stick is formed as I.
So, human eye at position E sees the end O at I; i.e., stick appears to be bent.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define focal length of a divergent lens.
A real image cannot be obtained on a screen.
State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
If a spherical lens has a power of, −0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) −4 cm
(b) −400 mm
(c) −4 m
(d) −40 cm
If a spherical lens has a power of, −0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) −4 cm
(b) −400 mm
(c) −4 m
(d) −40 cm
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Where is the object placed in front of the lens?
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the nature of image.
My grandfather uses a bifocal lens in his spectacle. Explain why.
Complete the ray diagram to show how the rays pass into and out of the lens?

Complete the following table for convex lens:
| Sr. No. | Position of the object | Position of the image | Nature of the image |
| 1. | Beyond 2F1 | __________________ | ________________________ |
| 2. | __________________ | At infinity | ________________________ |
| 3. | __________________ | __________________ | Real, inverted and enlarged |
