Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will such a lens produce an image of the complete object? Support your answer with a ray diagram.
Solution
The convex lens will form complete image of an object, even if its one half is covered with black paper. It can be understood by the following two cases:
Case I
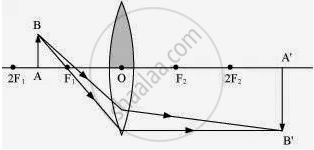
When the upper half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the above figure.
Case II
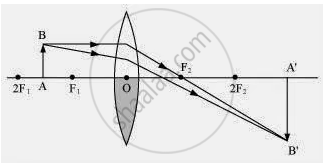
When the lower half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the above figure.
RELATED QUESTIONS
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
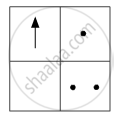
(a)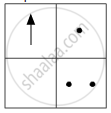
(b)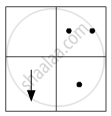
(c)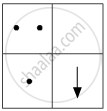
(d)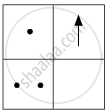
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Define principal axis, principal focus and focal length of a convex lens.
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
List some things that convex lens and concave mirror have in common.
Name one simple optical instrument in which the above arrangement of convex lens is used.
Describe the nature of image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
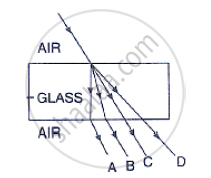
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object?
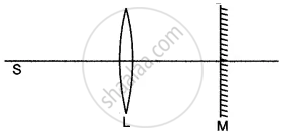
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
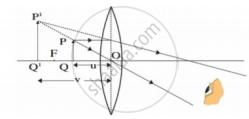 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 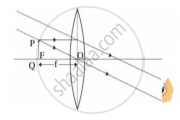
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
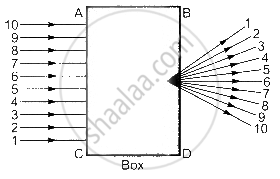
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
