Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
List some things that convex lens and concave mirror have in common.
Solution
Both form a virtual, erect and magnified image when the object is placed between the pole and focus of a convex mirror, and between the centre of the lens and the focus, for a concave lens.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
A convex lens of focal length 0.10 m is used to form a magnified image of an object of height 5 mm placed at a distance of 0.08 m from the lens. Calculate the position, nature and size of the image.
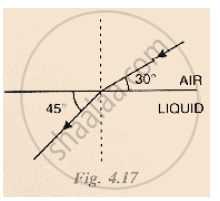
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
