Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how a concave lens diverges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the concave lens on the diagram.
Solution
When a parallel beam of light rays falls on a concave lens, the rays spread out (or diverge) after passing through the lens (figure). Since the refracted rays are diverging away from one another, they do not actually meet at a point. The diverging rays, when produced backwards appear to meet at a point F called the principal focus, on the left side of the lens.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be ______.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
In the concave reflector of a torch, the bulb is placed:
(a) between the pole and focus of reflector
(b) at the focus of reflector
(c) between focus and centre of curvature of reflector
(d) at the centre of curvature of reflector
When an object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror, its image is formed at 10 cm in front of the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
When an object is at the centre of curvature of concave mirror the image formed will be virtual and erect.
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

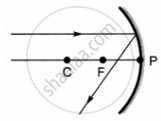 |
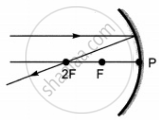 |
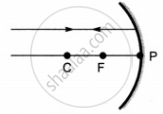 |
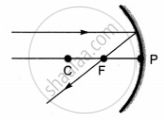 |
| A | B | C | D |
The mirror having reflecting surface curved inwards ______.
