Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Solution
Object placed at C :
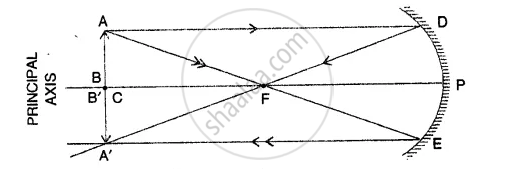
A real, inverted image of the same size is formed at the centre of curvature
Image formed
A ‘B’ is at C the centre of curvature.
Size is equal to the size of object AB.
It is inverted and real.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
The image formed by a concave mirror is of the same size as the object, if the object is placed
A student has to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object on a screen. For getting best result he should focus
(A) a distant tree or an electric pole
(B) a well-illuminated distant building
(C) well-lit grills of the nearest window
(D) a burning candle laced at the distant edge of the laboratory table
The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is _______.
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
