Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
उत्तर
Object placed at C :
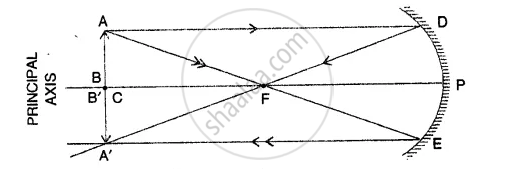
A real, inverted image of the same size is formed at the centre of curvature
Image formed
A ‘B’ is at C the centre of curvature.
Size is equal to the size of object AB.
It is inverted and real.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
A concave mirror cannot be used as:
(a) a magnifying mirror
(b) a torch reflector
(c) a dentist's mirror
(d) a real view mirror
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
A student obtained a sharp image of the grills of a window on a screen using a concave mirror. His teacher remarked that for getting better results a well lit distant object (preferably the sun) should be focussed on the screen. What should be done for this purpose?
(A) Move the screen slightly away from the mirror
(B) Move the mirror slightly towards the screen
(C) Move the screen and the mirror away from the object
(D) Move the screen and the mirror towards the object
Choose the correct option from given alternative:
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(A) cannot be projected on the screen
(B) are formed by both concave and convex lens
(C) are always erect
(D) are always inverted
You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
