Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
उत्तर
When an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, a real, inverted and diminished image of the object is formed.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also justify your answer. Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams
What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, −20 cm?
A concave mirror produces a real image 1 cm tall of an object 2.5 mm tall placed 5 cm from the mirror. Find the position of the image and the focal length of the mirror.
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it:
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
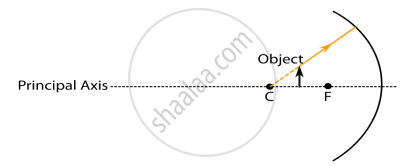
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following.
- the image of the object will be a virtual one.
- the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- the image of the object will be inverted.
- this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
Define principal focus of the concave mirror.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
