Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it:
उत्तर
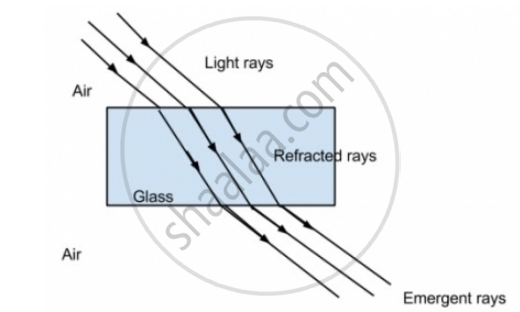
When a beam of light rays enters the glass block, it gets refracted. It bends towards the normal. Also, when these light rays leave the block, they bend away from the normal.
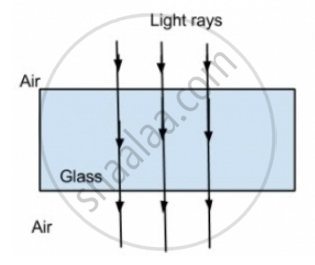
When light rays fall normally on the surface of the glass block, there is no bending of rays; the rays travel straight.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Described with the help of a diagram, the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
If an object is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm, discuss the nature of the image formed by drawing the ray diagram.
Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
The mirror having reflecting surface curved inwards ______.
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
