Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
उत्तर
The two rays chosen to construct a ray diagram are shown in the ray diagram given below

(i) Ray I: When the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will pass through the focus of concave mirror or it appears to pass through the focus of convex mirror.
(ii) Ray II: When the incident ray passes through or appears to pass through the centre of curvature, the light, after reflection from the spherical mirror, reflects back along the same path.
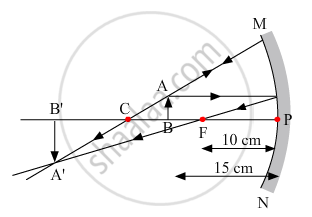
The image formed is real, inverted and magnified. It is formed beyond the centre of curvature.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 48 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 12 cm from its pole.
(a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(c) How far is the image from its object?
(d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Headlights of a car
Support your answer with reason.
Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
Give two uses of concave mirrors. Explain why you would choose concave mirrors for these uses.
An object is 24 cm away from a concave mirror and its image is 16 cm from the mirror. Find the focal length and radius of curvature of the mirror, and the magnification of the image.
If a concave mirror has a focal length of 10 cm, find the two positions where an object can be placed to give, in each case, an image twice the height of the object.
Suppose you have three concave mirrors A, B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distance of 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. Giving reason answer the following:
(a) For the three object distances, identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification – 1.
(b) Out of the three mirrors identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purposes/makeup.
(c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
What is a concave and convex mirror?
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
