Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
Solution
The two rays chosen to construct a ray diagram are shown in the ray diagram given below

(i) Ray I: When the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will pass through the focus of concave mirror or it appears to pass through the focus of convex mirror.
(ii) Ray II: When the incident ray passes through or appears to pass through the centre of curvature, the light, after reflection from the spherical mirror, reflects back along the same path.
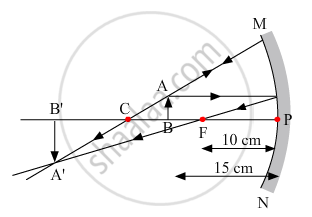
The image formed is real, inverted and magnified. It is formed beyond the centre of curvature.
RELATED QUESTIONS
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
Described with the help of a diagram, the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Explain why, concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
A man holds a spherical shaving mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, and focal length 30 cm, at a distance of 15 cm, from his nose. Find the position of image, and calculate the magnification.
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
Choose the correct option from given alternative:
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(A) cannot be projected on the screen
(B) are formed by both concave and convex lens
(C) are always erect
(D) are always inverted
______ mirrors make things look larger when objects are placed close to them.
Between which two points of a concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of -2?
