Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in Floodlight.
Solution
In a floodlight, the light source is slightly beyond the radius of curvature, which gives us the right light.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of an appropriate ray diagram, state the sign conventions for reflection by a spherical mirror.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror?
Draw the following diagram in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror on your answer sheet. Show the path of this ray, after reflection, in each case.

A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
The angle between an incident ray and the plane mirror is 30°. The total angle between the incident ray and reflected ray will be:
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
If the focal length of a convex mirror is 25 cm, what is its radius of curvature?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are reflected by a concave mirror to a point called the ..........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ......... to the mirror.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A concave mirror .......... rays of light whereas convex mirror ............ rays
Explain why, a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path.
Described with the help of a diagram, the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
Which mirror is used as a torch reflector? Draw a labelled diagram to show how a torch reflector can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Where is the bulb placed in relation to the torch reflector?
State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
(b) at infinity.
(c) the same size as the object.
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a virtual image by a converging mirror.
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature and position of object in each case.
Briefly describe how you would find the focal length of a concave mirror quickly but approximately
Which type of mirror is used in a solar furnace? Support your answer with reason.
Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
between its pole and focus
Describe the nature, size and position of the image formed in each case.
State one use of concave mirror bases on the formation of image as in case (i) above.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when object is:
(a) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(b) at a distance less than the focal length
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
An object is 100 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an upright (erect image). The radius of curvature of the mirror is ______.
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
According to New Cartesian Sign Convention:
(a) focal length of concave mirror is positive and that of convex mirror is negative
(b) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is positive
(c) focal length of both concave and convex mirrors is negative
(d) focal length of concave mirror is negative and that of convex mirror is positive
Write down a formula for the magnification produced by a concave mirror.
in terms of height of object and height of image
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Between which two points of concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of:
(a) −3
(b) +25
(c) −0.4
If a concave mirror has a focal length of 10 cm, find the two positions where an object can be placed to give, in each case, an image twice the height of the object.
Name the mirror which can give:
an erect and enlarged image of an object.
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
(a) concave or convex
(b) concave or plane
(c) convex or plane
(d) only convex
A concave mirror cannot be used as:
(a) a magnifying mirror
(b) a torch reflector
(c) a dentist's mirror
(d) a real view mirror
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it:
Why does a beam of light when it enters glass at an angle? Why does it not bend if it inters the glass at right angles?
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light from a bulb falls on it?
(a) concave mirror as well as concave lens
(b) convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c) concave mirror as well as convex lens
(d) concave mirror as well as convex lens
A convex mirror is used as a shaving mirror.
A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on a screen placed in front of the concave mirror. He then removed the screen and tried to look into the mirror. He would now see
(A) a very blurred image on the wall opposite to the mirror
(B) an erect and magnified image of the tree in the mirror
(C) no image as the screen has been removed
(D) a highly diminished inverted image of the tree at the focus of the mirror.
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
According to cartesion sign convention, which mirror and which lens has negative focal length?
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

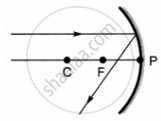 |
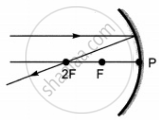 |
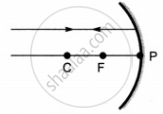 |
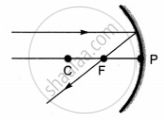 |
| A | B | C | D |
For a real object, which of the following can produce a real image?
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
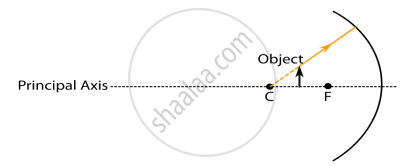
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following.
- the image of the object will be a virtual one.
- the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- the image of the object will be inverted.
- this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
The ENT doctor uses a ______.
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
What is a concave and convex mirror?
