Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in Floodlight.
उत्तर
In a floodlight, the light source is slightly beyond the radius of curvature, which gives us the right light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
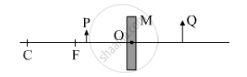
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed?
(A) Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(B) Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade
(C) Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(D) Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade
Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
A 3 cm tall object is placed 18 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to see a sharp image of the object on the screen. Also calculate the height of the image formed.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ......... to the mirror.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A concave mirror .......... rays of light whereas convex mirror ............ rays
Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the concave mirror.
For what position of an object, a real and diminished image is formed by a concave mirror?
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
If an object is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm, discuss the nature of the image formed by drawing the ray diagram.
With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a real image by a converging mirror.
Explain why, concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors.
In the concave reflector of a torch, the bulb is placed:
(a) between the pole and focus of reflector
(b) at the focus of reflector
(c) between focus and centre of curvature of reflector
(d) at the centre of curvature of reflector
Giving reasons, state the 'signs' (positive or negative) which can be given to the following:
(a) object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror
(b) image distance (v) for a concave mirror
(c) image distance (v) for a convex mirror
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a converging mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature, and size of the image formed.
An object of 5.0 cm size is placed at a distance of 20.0 cm from a converging mirror of focal length 15.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to get the sharp image? Also calculate the size of the image.
How far should an object be placed from the pole of a converging mirror of focal length 20cm to form a real image of the size exactly `1/4`th the size of the object?
An object is placed just outside the principal focus of concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and describe its size, position and nature.
An object is 24 cm away from a concave mirror and its image is 16 cm from the mirror. Find the focal length and radius of curvature of the mirror, and the magnification of the image.
Name the mirror which can give:
an erect and enlarged image of an object.
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is:
(a) convex mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) concave mirror
(d) both convex and concave mirror
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
Why does a beam of light when it enters glass at an angle? Why does it not bend if it inters the glass at right angles?
Name the lens which can concentrate sun's rays to a point and burn a hole in a piece of paper.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light from a bulb falls on it?
(a) concave mirror as well as concave lens
(b) convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c) concave mirror as well as convex lens
(d) concave mirror as well as convex lens
A convex mirror is used as a shaving mirror.
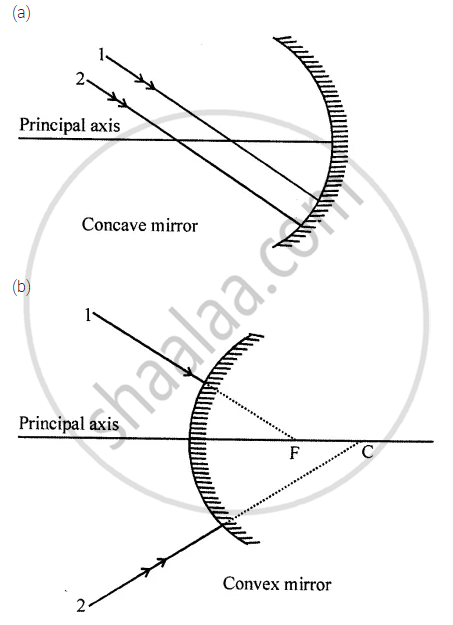
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
A student obtained a sharp image of the grills of a window on a screen using a concave mirror. His teacher remarked that for getting better results a well lit distant object (preferably the sun) should be focussed on the screen. What should be done for this purpose?
(A) Move the screen slightly away from the mirror
(B) Move the mirror slightly towards the screen
(C) Move the screen and the mirror away from the object
(D) Move the screen and the mirror towards the object
A _____________ mirror is used by a dentist.
In which equipment/s do you find ___________________
Choose the correct option from given alternative:
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(A) cannot be projected on the screen
(B) are formed by both concave and convex lens
(C) are always erect
(D) are always inverted
The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is _______.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
When an object is at the centre of curvature of concave mirror the image formed will be virtual and erect.
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at ______.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
In the headlights of motor vehicles, ______ mirrors are used as reflectors.
The focal length of a concave mirror is 5cm. Its radius of curvature is ______.
Write the uses of the concave mirror.
To obtain an image twice the size of the object, between which two points related to a concave mirror should an object be placed?
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Shaving mirror
