Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
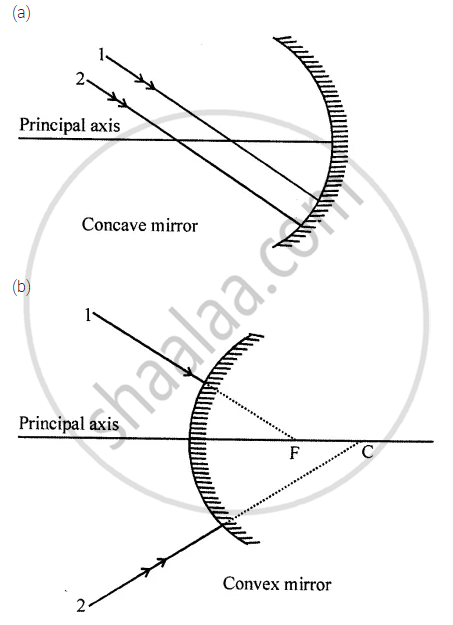
उत्तर
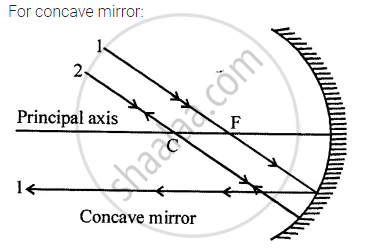
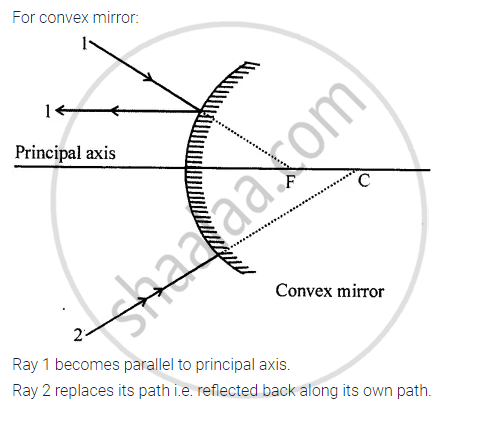
1. Ray passing through F after reflection becomes parallel to the principal axis.
Ray (2) passing through the centre of curvature travels back (retraces its path) i.e. reflected back along its own path.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed using the lens formula.
ill in the following blank with suitable word:
For a convex mirror, parallel rays of light appear to diverge from a point called the ......... .
If an object is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm, discuss the nature of the image formed by drawing the ray diagram.
State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
(b) at infinity.
(c) the same size as the object.
Between which two points of concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of:
(a) −3
(b) +25
(c) −0.4
The image formed by a concave mirror is of the same size as the object, if the object is placed
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Study the following ray diagram and list two mistakes committed by the student while tracing it. Rectify these mistakes by drawing the correct ray diagram to show the real position and size of the image corresponding to the position of the object AB.

An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
