Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
Solution
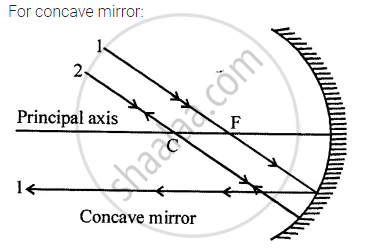
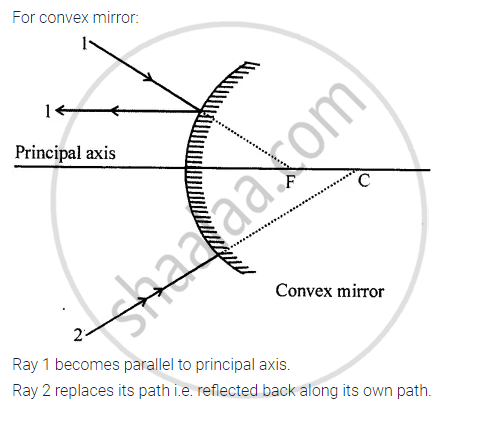
1. Ray passing through F after reflection becomes parallel to the principal axis.
Ray (2) passing through the centre of curvature travels back (retraces its path) i.e. reflected back along its own path.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). The object must be:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at focus
(c) at the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
A large concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 1.5 m. A person stands 10 m in front of the mirror. Where is the person's image?
An object of 5.0 cm size is placed at a distance of 20.0 cm from a converging mirror of focal length 15.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to get the sharp image? Also calculate the size of the image.
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
