Advertisements
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 5 - Light Energy Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 5 - Light Energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-8-icse_6:53235d1491ff438fb024a108557878b3.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Light Energy
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CISCE Selina for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 5 Light Energy Objective Questions
Write true or false
Water is optically denser than glass.
True
False
A ray of light when passes from glass to air, bends towards the normal.
True
False
The speed of light is more in glass than in water.
True
False
The depth of a pond when seen from above appears to be less.
True
False
Light travels at a lower speed in water than in air.
True
False
Light travels in the same straight line path while passing through different media.
True
False
At the point of incidence, a line drawn at right angles to the surface, separating the two media, is called the normal.
True
False
The angle formed between the normal and the refracted ray is known as the angle of incidence.
True
False
Image is formed by a mirror due to refraction of light.
True
False
Rays of light incident parallel to the principal axis pass through the focus after reflection from a concave mirror.
True
False
A convex mirror is used as a shaving mirror.
True
False
The focal length of a convex mirror is equal to its radius of curvature.
True
False
A concave mirror converges the light-rays, but a convex mirror diverges them.
True
False
A virtual image formed by a spherical mirror is always erect and situated behind the mirror.
True
False
Water is optically .......... than air.
Air is optically .......... than glass.
When a ray of light travels from water to air, it bends ............. the normal.
When a ray of light travels from air to glass, it bends .......... the normal.
When white light passes through a prism, it ............
The splitting of white light into its constituent colours is called .............
A .............. mirror is obtained on silvering the outer surface of a part of a hollow glass sphere.
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is ............. its focal length.
The angle of incidence for a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is ...........
A ............ mirror always forms a virtual image.
A concave mirror forms a virtual image for an object placed ...............................
Match the Following
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) white Light | (1) Convex mirror |
| (b) Refraction | (2) Concave mirror |
| (c) Virtual images | (3) refraction |
| (d) Real images | (4) spectrum |
| (e) Prism | (5) ray of light from glass to air |
Select the correct alternative
The speed of light in air or vacuum is
3 × 108 M s-1
2.25 × 108 m s-1
332 ms-1
2.0 × 108 ms-1
A ray of light moving from an optically rarer to a denser medium
bends away from the normal
bends towards the normal
remains undeviated
none of the above
The angle between the normal and refracted ray is called
angle of deviation
angle of incidence
angle of refraction
the angle of emergence.
The property of splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours is known as
rectilinear propagation
refraction
reflection
dispersion
The seven colours in the spectrum of sunlight in order, are represented as :
VIBGYOR
VIGYBOR
BIVGYOR
RYOBIVG
A ray of light passing through centre of curvature of a spherical mirror, after reflection
passes through the focus
passes through the pole
becomes parallel to the principal axis
retraces its own path.
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
10 cm
20 cm
40 cm
80 cm
The image formed by a convex mirror is
erect and diminished
erect and enlarged
inverted and diminished
inverted and enlarged.
The image formed by a concave mirror is of the same size as the object, if the object is placed
at the focus
between the pole and focus
between the focus and centre of curvature
at the centre of curvature.
A convex mirror is used
as a shaving mirror
as a head mirror by a dentist
as a rear view mirror by a driver
as a reflector in torch
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 5 Light Energy Short/long Answer Question [Pages 99 - 101]
State the speed of light in (a) air, (b) water, and (c) glass
How does the speed of light determine the optical density of a medium?
Which is optically denser: water or air? Give reason
Out of air and glass, which is optically rarer? Give reason.
What do you understand by refraction of light?
Describe an experiment to show that a light ray bends when it passes from one transparent medium into another transparent medium.
Draw a ray diagram to show that the depth of a vessel containing water when seen from above, appears to be less than its real depth.
Define the following terms :
Incident ray, Refracted ray, Angle of incidence, Angle of refraction.
A ray of light falls normally on a glass slab. What is the angle of incidence?
A ray of light travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium. How will it bend?
A ray of light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. How will it bend?
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
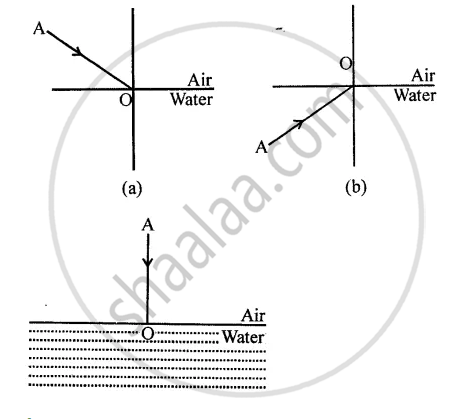
Draw a diagram showing the refraction of a light ray from water to glass. Label on it the incident ray, the angle of incidence (/), and the angle of refraction (r)
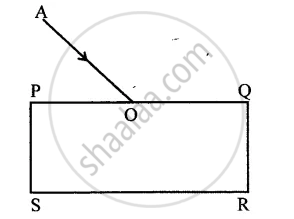
The diagram in figure shows a ray of light AO falling on a rectangular glass slab PQRS. Complete the diagram till the ray of light emerges out of the slab. Label on the diagram the incident ray, the refracted ray and the emergent ray.
Explain the following
A coin placed at the bottom of a vessel appears to be raised when water is poured in the vessel.
A straight stick partly dipped in water obliquely, appears to be bent at the surface of water.
The sun is seen before the sunrise and after the sunset.
What is mirage? Give a reason for its formation?
What is a prism?
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a light ray through a prism.
What do you mean by the term dispersion?
A ray of white light falls on a prism. Draw a ray diagram to show that the prism disperses the white light.
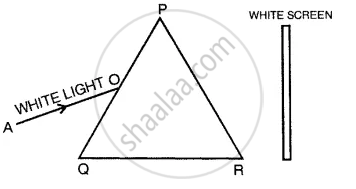
In figure AO is the ray of white light falling on a prism PQR. Complete the diagram till the light emerges out from the prism and falls on the screen.
What do you understand by the term spectrum? Name the various colours present in the spectrum of sunlight.
You are given a disc divided into seven sectors with colours violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red in them. What would be its colour when it is rotated rapidly?
State the two laws of reflection of light.
What is a spherical mirror?
State the two kinds of spherical mirror and distinguish them with the aid of proper diagrams.
Explain the following terms :
Pole, Centre of curvature, Radius of curvature, Principal axis. Show them on separate diagrams for each of the concave and convex mirrors.
What do you understand by the focus and focal length of a spherical mirror? Show them on the separate diagrams for each of a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate how a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis is reflected by:
(a) a concave mirror, and (b) a convex mirror
How is a spherical mirror used to converge a beam of light at a point? Name the type of mirror used.
How is a spherical mirror used to diverge a beam of light from a point? Name the type of mirror used.
State the direction of incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror gets reflected along its own path. Give a reason.
How is the focal length of a spherical mirror related to its radius
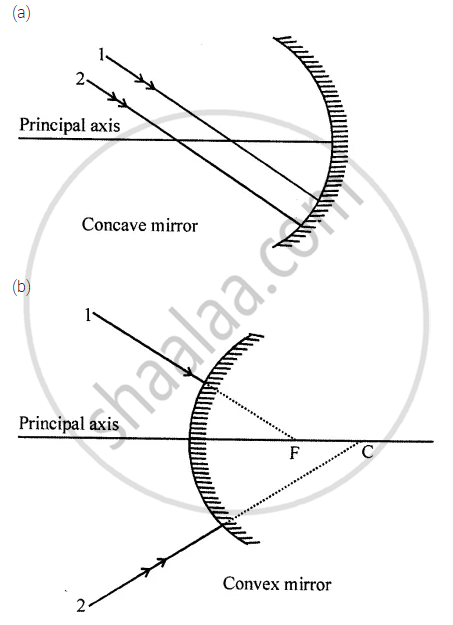
The diagram (figure) given below shows two parallel rays 1 and 2 incident on (a) a concave mirror, (b) a convex mirror. Draw the reflected rays and mark the focus by the symbol F.
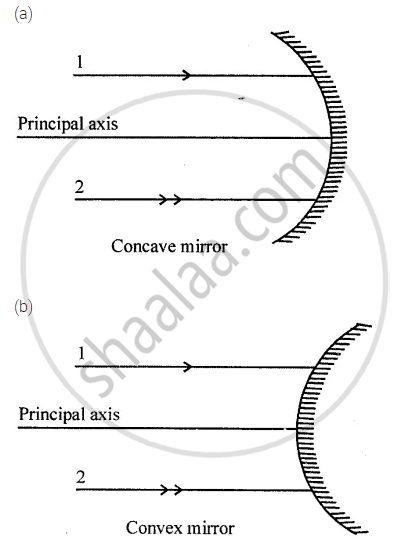
Complete the following diagrams in figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2 if F is the focus and C is the centre of curvature.
Which are the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the focus and centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
Draw separate diagram for the formation of virtual image of an object by a concave mirror.
Draw separate diagram for the formation of virtual image of an object by a convex mirror.
State the difference between concave mirror and convex mirror.
Name the mirror which always forms an erect and virtual image. What is the size of the image as compared to that of the object?
Name the mirror which forms an erect, virtual and enlarged image of an object. What is the position of object relative to the mirror?
What is a real image? Name the mirror which can be used to obtain the real image of an object. What should be the position of the object relative to the mirror?
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
State two uses of a concave mirror.
State two uses of a convex mirror.
A driver uses a convex mirror as a rearview mirror. Explain the reason with the help of a ray diagram.
State the kind of mirror used
(a) by a dentist, and
(b) as a street light reflector.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain
(a) a real and enlarged image
(b) a virtual and enlarged image
(c) a real and diminished image, and
(d) a virtual and diminished image.
Solutions for 5: Light Energy
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 5 - Light Energy Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 5 - Light Energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-8-icse_6:53235d1491ff438fb024a108557878b3.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 5 - Light Energy
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE CISCE 5 (Light Energy) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 5 Light Energy are Introduction to Refraction of Light, Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum, Spherical Mirrors, Some Terms Related to Refraction of Light, Atmospheric Refraction, Application of Atmospheric Refraction, Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab, Refraction of Light Through a Prism, Effects of Refraction, Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror, Image Formation by Convex Mirror, Image Formation by Concave Mirror, Speed of Light, Prism, Dispersion of Light and Its Causes, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Convex Mirror, Concave Mirror.
Using Selina Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE solutions Light Energy exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Light Energy Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
