Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
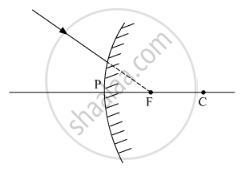
A ray of light passing through centre of curvature of a spherical mirror, after reflection
Options
passes through the focus
passes through the pole
becomes parallel to the principal axis
retraces its own path.
Solution
retraces its own path.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A mirror forms an image which is 30 cm from an object and twice its height.
(a) Where must the mirror be situated?
(b) What is the radius of curvature?
(c) Is the mirror convex or concave?
What is the advantage of using a convex mirror as rear-view mirror in vehicles as compared to a plane mirror? Illustrate your answer with the help of labelled diagrams.
A convex mirror used as a rear-view mirror in a car has a radius of curvature of 3 m. If a bus is located at a distance of 5 m from this mirror, find the position of image. What is the nature of the image?
Draw a diagram to represent a convex mirror. On this diagram mark principal axis, principal focus F and the centre of C if the focal length of convex mirror is 3 cm.
Write true or false
The focal length of a convex mirror is equal to its radius of curvature.
Numerical problem.
A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of an object placed at 7 cm in front of it. Where is the image located? (Ans: 21 cm in front of the mirror)
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between the focus and device, image formed is enlarged and on the same side as that of the object.
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between pole and focus, behind it.
Assertion: A real image cannot be produced by plane or convex mirror.
Reason: The focal length of a convex mirror is always taken as positive.
