Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-8-icse_6:53235d1491ff438fb024a108557878b3.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Electricity
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CISCE Selina for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 8 Electricity Exercise 8 (A) (Objective questions) [Pages 150 - 151]
A fuse wire has a high melting point.
True
False
Flow of protons constitutes electric current.
True
False
Silver is an insulator of electricity.
True
False
S.I. unit and commercial unit of electrical energy are same.
True
False
Overloading of electric current in circuits can lead to short-circuiting.
True
False
All metals are insulators of electricity.
True
False
The earth wire protects us from an electric shock.
True
False
A switch should not be touched with wet hands.
True
False
All electrical appliances in a household circuit work at the same voltage.
True
False
In a cable, the green wire is the live wire.
True
False
A fuse is connected to the live wire.
True
False
A switch is connected to the neutral wire.
True
False
Our body can pass electricity through it.
True
False
The unit in which we pay the cost of electricity is ..........
The electrical energy consumed in a house is measured by ...............
In a household electrical circuit, the appliance are connected in ............with the mains.
A switch is connected to the .......... wire.
The red colour insulated wire in a cable is the .............. wire.
One kilowatt hour is equal to ............ joule.
A fuse wire should have low .................
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| Electric power | volt |
| kWh | joule |
| Electric current | volt × ampere |
| Electric energy | watt |
| watt | ampere |
| potential difference | electrical energy |
All wires used in electric circuits should be covered with
colouring material
conducting material
an insulating material
none of the above
Electric work done per unit time is ____________.
electrical energy
electric current
electric voltage
electrical power
One kilowatt is equal to
100 watt
1000 watt
10 watt
none of these
Fuse wire is an alloy of
tin-lead
copper-lead
tin-copper
lead-silver
A fuse wire should have
a low melting point
high melting point
very high melting point
none of the above
When the switch of an electric appliance is put off, it disconnects
the live wire
the neutral wire
the earth wire
the live and the neutral wire
The purpose of an electric meter in a house is
to give the cost of electricity directly
to give the consumption of electrical energy
to safeguard the circuit from short circuiting
to put on or off the mains.
If out of the two lighted bulbs in a room, one bulb suddenly fuses, then
other bulb will glow more
other bulb will glow less
other bulb will also fuse
other bulb will remain lighted unaffected.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 8 Electricity Exercise 8 (A) (Short/Long answer questions) [Pages 151 - 152]
From where does the electricity come to our home ?
What is an electric meter? Where is it fixed in our house?
State the purpose of kWh meter.
For which unit do we pay our electricity bill?
How can you check just by seeing the meter whether the electricity is in use or not?
The diagram below in figure shows the reading on the dials of a meter. State what is its reading.
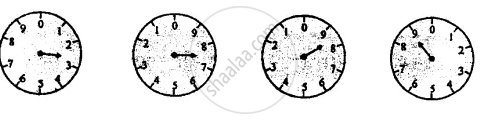
One day the meter reading is found to be 7643 units while the next day, it was 7657 units. What is the consumption of electricity in a day?
A source of potential difference V volt sends current I ampere in a circuit for time t second. Write expressions for
- electrical energy supplied by the source and
- electrical power spent by the source.
Name the unit in which you pay the cost of your electricity bill. How is it related to joule?
If an appliance of power P watt is used for time t hour. How much electrical energy is consumed in kWh?
What is an electric fuse? State its purpose in the household electrical circuit.
State one property of the material of a fuse wire.
Name the material of a fuse wire.
Can we use copper wire as a fuse wire? Give reason.
How does a fuse protect the electric wiring (or an appliance) from being damaged?
Which fuse wire is thick: 5 A or 15 A?
Write the full form of M.C.B?
How is M.C.B. superior to the fuse wire?
With which wire: live or neutral is the fuse wire connected?
What do you mean by short-circuiting of a circuit?
Figure shows two ways of connecting the three bulbs A, B and C to a battery. Name the two arrangements. Which of them do you prefer to use in a household circuit? Give a reason to support your answer.
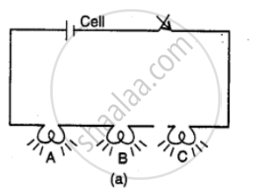
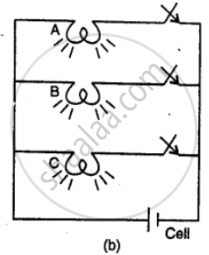
How are the electrical appliances connected in a house circuit: in series or in parallel? Give reason.
In the household electric circuit, if one bulb is fused in a room, the other bulbs keep glowing. Explain the reason.
State the voltage at which electricity is supplied to our houses.
Draw a labelled diagram with the necessary switches to connect a bulb, a fan and a plug socket in a room with the mains. In what arrangement will you connect them to the mains?
State the colour coding of the three wires in a cable used for
Why is the metal covering of an electrical appliance earthed?
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 8 Electricity Exercise 8 (A) (Numericals) [Page 152]
An electrical appliance is rated as 60 W – 150 V.
What do you understand by this statement?
An electrical appliance is rated as 60 W – 150 V.
How much current will flow through the appliance when in use?
An electric iron of power 1.5 kW is used for 30 minutes to press the clothes. Calculate the electrical energy consumed in
- kilowatt-hour
- joule.
Assuming the electric consumption per day to be 12 kWh and the rate of electricity to be? 6.25 per unit, find how much money is to be paid in a month of 30 days?
In a premise 5 bulbs each of 100 W, 2 fans each of 60 W, 2 A.Cs each of 1.5 kW is used for 5 h per day. Find:
- Total power consumed per day,
- Total power consumed in 30 days,
- Total electrical energy consumed in 30 days.
- The cost of electricity at the rate of ₹ 6.25 per unit.
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 8 Electricity Exercise 8 (B) (Objectives question) [Pages 165 - 166]
The number of electrons and protons in an atom are the same.
True
False
If the charge is not in motion, we call it static electricity.
True
False
Human body is a conductor of electricity.
True
False
When an ebonite rod is rubbed with fur, the electrons move from ebonite to fur.
True
False
When glass rod is rubbed with dry silk cloth, the electrons move from glass to silk.
True
False
The cap of gold leaf electroscope is made of copper.
True
False
If a glass rod rubbed with silk is brought near the cap of a negatively charged electroscope, the divergence of leaves will decrease.
True
False
In induction, a positively charged body can make an uncharged body positively charged.
True
False
A lightning conductor saves the building from lighting.
True
False
When a comb is rubbed with dry hair both comb and paper get similarly charged.
True
False
A glass rod rubbed with silk repels an ebonite rod rubbed with fur.
True
False
When an ebonite rod is rubbed with fur, the protons move from the ebonite rod to the fur.
True
False
A conductor has a large number of free electrons.
True
False
An ebonite rod can be charged by touching it with a charged copper rod.
True
False
To find whether a body is charged or not, an uncharged electroscope is used.
True
False
To find whether the charge on a body is positive or negative, an uncharged electroscope is used.
True
False
If a negatively charged rod is brought near a negatively charged pith ball electroscope, the pith ball will be stuck with the rod.
True
False
Like charges ............while unlike charges attract.
Mercury is a ............ of electricity while pure water is ............ of electricity.
An ebonite rod when rubbed with fur acquires the ............ charge.
When an uncharged conductor is brought in contact with the disc of a gold leaf electroscope, its leaves ....................
Charge is shared in charging a conductor by the method of ...............
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Two like charges | 1 negative charge |
| B. Two unlike charges |
2 repel |
| C. Silver is a | 3 insulator |
| D. Silk is an | 4 attract |
| E. Ebonite rod rubbed with fur acquires | 5 conductor |
When a glass rod is rubbed with dry silk cloth, the charge acquired by the silk cloth is
Positive
negative
both positive and negative
none of the above
When an ebonite rod is rubbed with fur, the rod acquires
positive charge
negative charge
no charge
none of the above
When a negatively charged body is brought closer to another negatively charged body, then they will show
attraction
no effect
repulsion
none of the above
Charging a conductor by bringing another charged conductor close to it without touching is called
induction
conduction
convection
radiation
The factor responsible for charging a conductor is
transfer of protons
transfer of neutrons
transfer of electrons
transfer of both protons and electrons
Two objects when rubbed together get charged. The charges on them are
equal and opposite
equal and similar
unequal and similar
unequal and opposite
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, the glass rod and the silk get charged because
electrons are transferred from the silk to the glass rod
electrons are transferred from the glass rod to the silk
protons are transferred from the silk to the glass rod
protons are transferred from the glass rod to the silk
The conductor of electricity is
wood
glass
ebonite
human body
A gold-leaf electroscope is to be charged positively by conduction. For this
a positively charged rod is held close to near the disc of electroscope
a positively charged rod is placed in contact with the disc of electroscope
a negatively charged rod is held near the disc of electroscope
a negatively charged rod is touched with the disc of electroscope.
A glass rod rubbed with silk is touched with the disc of a negatively charged gold leaf electroscope. The divergence of leaves will
decrease
increase
remain unchanged
first decrease and then increase.
The rod in a gold leaf electroscope is made up of
wood
brass
glass
ebonite
The lightning conductor is made up of:
copper
glass
ebonite
wood
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE 8 Electricity Exercise 8 (B) (Short/Long answer questions) [Pages 166 - 168]
What do you understand by electricity at rest?
Why does a plastic comb rubbed with dry hair attract bits of paper?
Who discovered the way of producing electricity by friction?
Name two substances which can be charged by friction.
What are the two kinds of charges?
A glass rod is rubbed with silk. State the kind of charge acquired by each.
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. State the kind of-charge acquired by each.
Describe an experiment to demonstrate that there are two r kinds of charges.
How will you show that like charges repel and unlike charges attract each other?
A glass rod rubbed with silk is suspended near an ebonite r rod rubbed with fur. What will be your observation? Give a reason to your answer.
An ebonite rod rubbed with fur is suspended near another ebonite rod rubbed with fur. State your observation and give a reason to support your answer.
What do you mean by conservation of charges?
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. Compare the charges acquired by them.
Name three constituents of an atom and state the kind of charge on each of them.
What is the net charge on an atom?
Briefly describe the structure of an atom.
What are free electrons?
What causes the charging of two objects when they are rubbed together?
In each of the following cases, State which body loses electrons:
(a) A glass rod when rubbed with silk.
(b) An ebonite rod when rubbed with fur.
A glass rod is rubbed with silk. Explain the charging of the glass rod and the silk on the basis of electron movement.
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. Explain the charging of the ebonite rod and the fur on the basis of electron movement.
Distinguish between conductors and insulators of electricity.
Give one example each of a conductor and an insulator of electricity.
State two ways of charging a conductor.
Name the way of charging a conductor in which the charge is shared.
Describe the method of charging a conductor by conduction.
A metal rod A is to be charged positively by using another charged rod B. What should be the kind of charge on the rod B if charging is to be done by conduction?
Explain the charging by conduction in terms of movement of electrons.
Describe the method of charging a conductor by induction.
Explain the charging by induction in terms of movement of electrons.
Figure below shows a metal rod AB placed on an insulating stand.
In figure (a) a negatively charged ebonite rod C is touched with the metal rod AB, while in figure (b), the negatively charged ebonite rod C is held near the rod AB. State the kind of charges at the ends A and B of the rod, in each case.
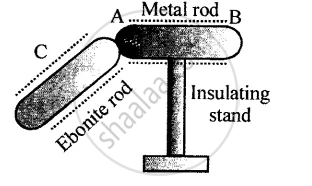
Can you charge an insulator by the method of conduction?
What is an electroscope?
Name the two types of electroscopes.
Describe a pith ball electroscope. how can you use it to test whether a body is charged or uncharged?
How will you use a pith ball electroscope to find out whether the charge on a charged body is positive or negative?
Draw a labelled diagram of a gold leaf electroscope and describe its construction.
A positively charged glass rod is touched with the disc of an uncharged gold leaf electroscope. What will be your observation?
How will you use a gold leaf electroscope to find out whether a body is charged or uncharged?
How will you use a gold leaf electroscope to find out whether the charge on a charged body is positive or negative?
A negatively charged ebonite rod is touched with the disc of a negatively charged gold leaf electroscope. What will be your observation?
When a charged rod is touched with the disc of a positively charged gold-leaf electroscope, it is observed that the divergence of leaves decreases. What is the kind of charge on the rod?
Describe Franklin’s experiment. What did he conclude from his experiment?
What causes lightning?
What are the effects of lightning?
What is a lightning conductor? How does it work?
How is a tall building protected from damage due to lightning?
State three safety measures that you will observe in thunder storm.
Solutions for 8: Electricity
![Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-physics-english-class-8-icse_6:53235d1491ff438fb024a108557878b3.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 8 - Electricity
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE CISCE 8 (Electricity) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE chapter 8 Electricity are Dangers of Electricity, Colour Coding of Live, Neutral, and Earth Wires, Earthing (Grounding), Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity, Electricity, Power Rating of Appliances, Electrical Energy and Power Consumed in a Circuit, Household Consumption of Electric Energy, Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer, Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), Household Electrical Circuits, Electric Circuit in a Room, Electric Meter, Commercial Unit of Electrical Energy, Electric Fuse, Lightning and Lightning Safety, Static Electricity, Electric Charge, Conductors and Insulators, Methods of Charging a Conductor, Electroscope, Types of Charges and Their Interaction, Transfer of Charges, Lightning and Lightning Safety, Static Electricity, Electric Charge, Conductors and Insulators, Methods of Charging a Conductor, Electroscope, Types of Charges and Their Interaction, Transfer of Charges.
Using Selina Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE solutions Electricity exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Electricity Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Physics [English] Class 8 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
