Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Distinguish between conductors and insulators of electricity.
Solution 1
DISTINCTIONS BETWEEN CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS OF ELECTRICITY:
| CONDUCTORS | INSULATORS |
| (i) They allow the current electricity to flow through them. | Do not allow the current electricity to flow through them. |
| (ii) They have a large number of free electrons. | They have a small number of free electrons. |
| (iii) All metals like Ag, Cu, iron, gold, wet wood etc. | Cotton, dry wood, rubber, glass distilled water etc. |
| (iv) Conductors cannot be charged by rubbing. | Can be charged by rubbing. |
Solution 2
DISTINCTIONS BETWEEN CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS OF ELECTRICITY:
| Basis For Comparison | Conductor | Insulator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Material which permits the electric current or heat to pass through it. | Restrict the electric current or heat to pass through it. |
| Electric Field | Exist on the surface but remain zero inside the conductor. | Do not exit on insulator. |
| Magnetic Field | Store energy | Do not store energy |
| Potential | Remain same at all the point on a conductor. | Remain zero. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Low |
| Covalent bond | Weak | Strong |
| Conductivity | Very high | Low |
| Resistance | Low | High |
| Electrons | Freely move | Do not move freely |
| Resistivity | Vary from high to low | High |
| Temperature coefficient | Positive temperature coefficient of resistance | Negative temperature coefficient of resistance |
| Conduction band | Full of electrons | Remain empty |
| Valence Band | Remains Empty | Full of electrons |
| Forbidden gap | No forbidden gap | Large forbidden gap |
| Examples | Irons, aluminium, silver, copper, etc. | Rubber, Wood, Paper, etc. |
| Application | For making electrical wires and conductor | As insulation in electrical cables or conductor, for supporting electrical equipment etc. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Silver is an insulator of electricity.
An electrical appliance is rated as 60 W – 150 V.
What do you understand by this statement?
An ebonite rod can be charged by touching it with a charged copper rod.
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Two like charges | 1 negative charge |
| B. Two unlike charges |
2 repel |
| C. Silver is a | 3 insulator |
| D. Silk is an | 4 attract |
| E. Ebonite rod rubbed with fur acquires | 5 conductor |
In each of the following cases, State which body loses electrons:
(a) A glass rod when rubbed with silk.
(b) An ebonite rod when rubbed with fur.
Explain the charging by induction in terms of movement of electrons.
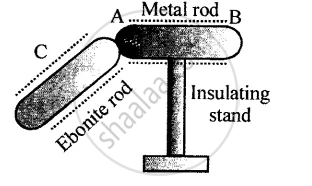
Figure below shows a metal rod AB placed on an insulating stand.
In figure (a) a negatively charged ebonite rod C is touched with the metal rod AB, while in figure (b), the negatively charged ebonite rod C is held near the rod AB. State the kind of charges at the ends A and B of the rod, in each case.
What causes lightning?
What is a lightning conductor? How does it work?
State three safety measures that you will observe in thunder storm.
