Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
Solution
OBJECT PLACED IN FRONT OF CONVEX MIRROR :

Place the object anywhere in front of convex mirror image formed is
- Between pole and focus ← position.
- Diminished ← size.
- Upright (erect) and virtual ← nature.
As the object is moved away from the mirror, the image shifts towards the focus and decreases in size but is (diminished)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
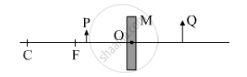
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image with the help of suitable rays:
Briefly describe how you would find the focal length of a concave mirror quickly but approximately
The real image formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when object is:
(a) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(b) at a distance less than the focal length
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
If an object of 10 cm height is placed at a distance of 36 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm, find the position, nature and height of the image.
Name the mirror which can give:
an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
Name the lens which can concentrate sun's rays to a point and burn a hole in a piece of paper.
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
