Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
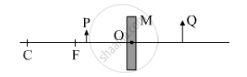
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
Solution
The given mirror M is a concave spherical mirror. The characteristic property of the image Q is that it is virtual.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a virtual image by a converging mirror.
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature and position of object in each case.
Briefly describe how you would find the focal length of a concave mirror quickly but approximately
What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, −20 cm?
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
