English Medium
Academic Year: 2015-2016
Date & Time: 2nd March 2016, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
Write the next homologue of the following: C2H4
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Write the next homologue of the following: C4H6
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List two natural ecosystems.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
List four advantages of properly managed watershed management.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Explain giving example where active involvement of local people lead to efficient management of forest.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
What are covalent compounds?
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Why covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds?
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
List three characteristic properties of covalent compounds.
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of conc. H2SO4, a substance with fruity smell is produced. Answer the following:-
(i) State the class of compounds to which the fruity smelling compounds belong. Write the chemical equation for the reaction and write the chemical name of the product formed.
(ii) State the role of conc. H2SO4 in the reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Calcium is an element with atomic number 20. Stating reason, answer each of the following questions:-
(i) Is calcium a metal or a non-metal?
(ii) Will its atomic radius be larger or smaller than that of potassium with atomic number 19?
(iii) Write the formula of its oxide.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
An element 'M' with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with (NO3)–, (SO4)2– and (PO4)3– radicals. Write the formula of the three compounds so formed. To which group and period of the Modern Periodic Table does the element 'M' belong? Will 'M' form covalent or ionic compounds? Give reason to justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations? Explain with the help of suitable example.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.

Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Suggest three contraceptive methods to control the size of human population, which is essential for the health and prosperity of a country. State the basic principle involved in each.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
In one of his experiments with pea plants, Mendel observed that when a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant in the first generation, F1, only tall plants appear.
(a) What happens to the traits of the dwarf plants in this case?
(b) When the F1-generation plants were self-fertilised, he observed that in the plants of the second generation, F2, both tall plants and dwarf plants were present. Why it happened? Explain briefly.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
List three distinguishing features, in tabular form, between acquired traits and the inherited traits.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Advertisements
Draw the following diagram in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror on your answer sheet. Show the path of this ray, after reflection, in each case.

Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this phenomenon be observed by an observer on the moon? Justify your answer with a reason.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Give reason to justify the following: The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Give reason to justify the following: Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Give a chemical test to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Name the products formed when ethane burns in the air. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction showing the types of energies liberated.
Chapter:
Why is the reaction between methane and chlorine in the presence of sunlight considered a substitution reaction?
Chapter:
Write the functions of the following parts in human female reproductive system:-
(i) Ovary
(ii) Oviduct
(iii) Uterus
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe placenta structure.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe the function of placenta.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List four factors that could lead to speciation. Which of them cannot be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollinating plant species?. Give reason to justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Pole
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Centre of curvature
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal axis
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Principal focus
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a convex mirror.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
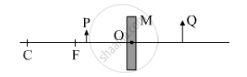
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Advertisements
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: Cornea
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write the function of the following part of the human eye:- iris
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: crystalline lens
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: ciliary muscles
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Millions of people in the developing countries of the world are suffering from corneal blindness. These persons can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. A charitable society of your city has organised a campaign in your neighbourhood in order to create awareness about this fact. If you are asked to participate in this mission, how would you contribute in this noble cause?
(i) State the objective of organising such campaigns.
(ii) List two arguments which you would give to motivate the people to donate their eyes after death.
(iii) List two values which are developed in the persons who actively participate and contribute in such programmes.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Which of the following sets of materials can be used for conducting a saponification reaction for the preparation of soap?
(a) Ca(OH)2 and neem oil
(b) NaOH and neem oil
(c) NaOH and mineral oil
(d) Ca(OH)2 and mineral oil
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student takes four test tubes marked P, Q, R and S of 25 mL capacity and fills 10 mL of distilled water in each. He dissolves one spoon full of four different salts in each as − KCl in P, NaCl in Q, CaCl2 in R and MgCl2 in S. He then adds about 2 mL of a sample of soap solution to each of the above test tubes. On shaking the contents of each of the test tubes, he is likely to observe a good amount of lather (foam) in the test tubes marked
(a) P and Q
(b) R and S
(c) P, Q and R
(d) P, Q and S
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Consider the following comments about saponification reactions:
I. Heat is evolved in these reactions.
II. For quick precipitation of soap, sodium chloride is added to the reaction mixtures.
III. Saponification reactions are a special kind of neutralisation reactions.
IV. Soaps are basic salts of long-chain fatty acids.
The correct comments are
(a) I, II and III
(b) II, III and IV
(c) I, II and IV
(d) Only I and IV
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student has to perform the experiment "To identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed." Select from the following an appropriate group of seeds:
(a) Pea, gram, wheat
(b) Red kidney bean, maize, gram
(c) Maize, wheat, red kidney bean
(d) Red kidney bean, pea, gram
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Which of the following is a correct set of homologous organs?
(a) Forelimbs of frog, bird and lizard
(b) Spine of cactus and thorn of bougainvillea
(c) Wings of bat and wings of butterfly
(d) Wings of a bird and wings of a bat
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
To determine the approximate focal length of the given convex lens by focussing a distant object (say, a sign board), you try to focus the image of the object on a screen. The image you obtain on the screen is always
(a) erect and laterally inverted
(b) erect and diminished
(c) inverted and diminished
(d) virtual, inverted and diminished
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Select from the following the best experimental setup for tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
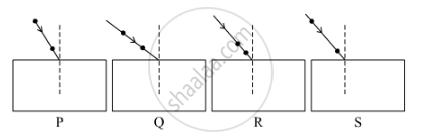
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Study the following figure in which a student has marked the angle of incidence (∠i), angle of refraction (∠r), angle of emergence (∠e), angle of prism (∠A) and the angle of deviation (∠D). The correctly marked angles are
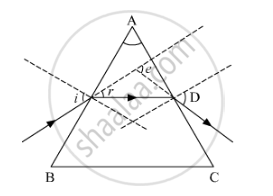
(a) ∠A and ∠i
(b) ∠A, ∠i and ∠r
(c) ∠A, ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠A, ∠i, ∠r and ∠D
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
What do you observe when you drop a few drops of acetic acid to test tubes containing
(a) phenolphthalein
(b) distilled water
(c) universal indicator
(d) sodium hydrogen carbonate powder
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Draw a labelled diagram to show that particular stage of binary fission in amoeba in which its nucleus elongates and divide into two and a constriction appears in its cell membrane.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2015 - 2016
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2016 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
