Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suggest three contraceptive methods to control the size of human population, which is essential for the health and prosperity of a country. State the basic principle involved in each.
Solution
Barrier method:- In this method, the fertilisation of the ovum and the sperm is prevented with the help of barriers such as a condom.
Oral contraceptive method:- In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally to prevent fertilisation.
Implants and surgical methods:- Contraceptive devices, such as a loop and a copper-T rod, are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. However, they can cause side effects to the uterus.
Some surgical methods such as vasectomy (blocking of the vas deferens in the male body to prevent the transfer of sperms) and tubectomy (blocking of fallopian tubes in the female body to prevent the egg from reaching the uterus) can also be used to block the gamete transfer.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the respective part of human female reproductive system:-
(i) that produces eggs,
(ii) where fusion of eggs and sperm takes place, and
(iii) where zygote gets implanted.
A single highly coiled tube where sperms are stored gets concentrated, and mature is known as ______
One of the following is not a part of the human male reproductive system. This is
(a) testis
(b) oviduct
(c) seminal vesicle
(d) prostrate gland
The normal body cell of an organism contains 28 pairs of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes present in its germ cell will be
(a) 28
(b) 14
(c) 56
(d) 42
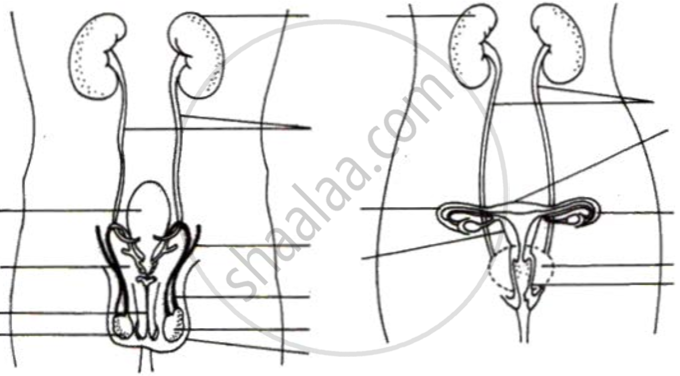
Draw a diagram to display the vertical view of human female reproductive system and label the following parts in the diagram:
(1) Ureter
(2) Ovary
(3) Funnel of fallopian tube
(4) Urethra.
Label the folowing diagram
Differentiate
Sexual Reproduction and Asexual Reproduction.
Name the Following
What does this abbreviation stand for IUD?
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Acrosome
(ii) Ovulation (iii) Sperm (iv) Menopause (v) Implantation (vi) Fertilization (vii) Contraception in males |
(a) Male gamete
(b) Oviduct (c) Uterus (d) Spermatozoa (e) Progesterone (f) Stoppage of the menstrual cycle (g) Sudden change in genes |
The living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from the non-living things on the basis of their ability for ______.
