Topics
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Structure and Events
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Stamen (Male Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Microsporangium
- Structure of Microspore Or Pollen Grain
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Pistil (Female Reproductive Unit)
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Megasporangium
- Pre-fertilization in Plant: Formation of Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Pollen Pistil Interaction
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Apomixis
- Parthenocarpy
- Polyembryony
- Kinds of Pollination
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Lactation in Human
- Reproductive Health
- Population Stabilisation and Birth Control
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Infertility
- Gastrulation in humans
Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Genes and Genetic
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Deviations from Mendel’s Findings
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Autosomal Inheritance
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Sex Determination
- Genetic Disorders
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- DNA Replication
- Protein Synthesis
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Genomics
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Genetic Code
Origin and Evolution of Life
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Chemical Evolution of Life (Self-assembly Theory of the Origin of Life)
- Darwinism
- Mutation Theory
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Adaptive Radiation
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Speciation
- Geological Time Scale
- Human Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
Plant Water Relation
- Plant Water Relation
- Properties of Water
- Water absorbing organ
- Water Available to Roots for Absorption
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Active Transport
- Passive Transport
- Water Potential (ψ)
- Path of Water Across the Root
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Structure of Stomatal Apparatus
- Significance of Transpiration
Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
- Plant Growth
- Phases of Plant Growth
- Conditions Necessary for Plant Growth
- Plant Growth Rate
- Plant Growth Curve
- Differentiation, De-differentiation, Re- Differentiation
- Plant Development
- Plant Plasticity
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Photoperiodism
- Vernalization (Yarovization)
- Plant Mineral Nutrition
- Nitrogen Cycle
Respiration and Circulation
- Respiration
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Regulation of Breathing / Respiration
- Modified Respiratory Movements
- Disorders of Respiratory System
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Circulation in Animals
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Human Heart
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Blood Vessels
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Mechanism of respiration - Internal respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - External respiration
- Mechanism of respiration - Cellular respiration
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination
- Nervous System in Hydra
- Nervous System in Planaria (Flatworm)
- Neural Tissue
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuroglial Cells (Or Glial Cells)
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Sensory Receptors
- Human Eye
- Human Ear
- Disorders of Nervous System
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- The Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- The Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Synapse - Types of synapse
- Transmission of nerve impulse
- Generation of nerve impulse
- Reflex Action
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Diffuse Endocrine Glands
Human Health and Diseases
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Structure of Antibody
- Disease
- Protozoan Diseases
- Helminthic Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Cancer
- Adolescence
- Addiction
- Drug Abuse
Enhancement of Food Production
- Improvement in Food Production
- Plant Breeding
- Tissue Culture
- Single Cell Protein (SCP)
- Biofortification
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Animal Breeding
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Apiculture (Bee Farming)
- Pisciculture (Fish Farming)
- Sericulture
- Lac Culture
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Energy Generation
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
Biotechnology
- Biotechnology
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Methodology for rDNA Technology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Bioethics
- Effects of Biotechnology on the Environment
- Biopatent and Biopiracy
- Transgenic Plants
- Transgenic animals
- Effects of Biotechnology on Human Health
- Tools and techniques for gene cloning/ rDNA technology
Organisms and Populations
- Organisms and the Environment Around
- Habitat
- Niche
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Population
- Population Interactions
- Organisms and Populations
Ecosystems and Energy Flow
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Classification of Animal
- Trophic Level
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- Ecological Pyramids
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecological Succession
- Ecosystem Services
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
- Biodiversity
- Levels of Biodiversity
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Current Scenario
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Environmental Issues
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Noise Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Green House Effect
- Preventive Measures of Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Preventive Measures of Global Warming
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Mission Harit Maharashtra
- Conservation of Biodiversity
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Regulation of Kidney Function
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Human Reproduction
Human Reproduction:
- Human reproduction is any form of sexual reproduction resulting in human fertilization.
- The reproductive system is a system of organs that takes part in this process.
- Humans are sexually reproducing and viviparous.
- The rate of reproduction is slower in sexual reproduction.
- Humans are unisexual.
- The reproductive events in humans include the formation of gametes (gametogenesis), i.e., sperms in males and ovum in females, transfer of sperms into the female genital tract (insemination), and fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization) leading to the formation of zygote.
- This is followed by the formation and development of blastocyst and its attachment to the uterine wall (implantation), embryonic development (gestation), and delivery of the baby (parturition).
- The beginning of sexual maturity or the ability to reproduce is known as puberty. Puberty occurs at the age of 10 - 14 years in girls and 13 - 15 years in boys.
- There are remarkable differences between the reproductive events in the male and in the female, for example, sperm formation continues even in old men, but the formation of ovum ceases in women around the age of fifty years.
-
The reproductive system of each sex consists of many organs. The latter is distinguishable into primary and secondary sex organs. Besides these, there are some accessory sex characters.
- Primary sex organs: Primary sex organs are also called gonads which form gametes like - testis in males and ovary in females. Testis produces sperms and secretes testosterone. The ovary produces ova and secretes estrogen. The male gamete is a spermatozoon. The female gamete is the ovum.
- Secondary sex organs: Sex organs, glands, and ducts which do not produce gametes but are otherwise essential for sexual reproduction are known as secondary sex organs. In males, these include the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands, penis, etc. In females, these organs are the fallopian tube, uterus, vagina, Bartholin gland, etc.
- Accessory / External / Secondary sex characters: These are traits which do not have any direct role in reproduction but provide specific features and structures to both sexes.
REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEINGS:-
Humans use sexual mode of reproduction.
-Sexual maturation: The period of life when production of germ cells i.e. Ova (female) and sperm (male) start in the body. This period of sexual maturation is called puberty.
Changes at puberty:-
Male and females:-
-Thick hair growth in armpits and genital areas.
-Skin becomes oily, may result in pimples.
In females:-
-Breast size increases
-Girls begin to menstruate.
In males:-
-Thick hair growth on face
-voice begins to crack
These changes signal that sexual maturity is taking place
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM:-
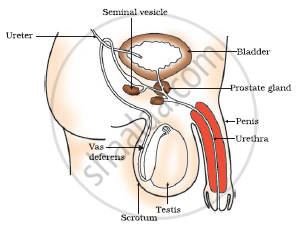
(i)Testes:-
-A pair of testes are located inside the scrotum which is present outside the abdominal cavity.
-scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production of sperms.
-male germ cell i.e. sperms are formed here.
-testes release male sex hormone (testosterone)
Functions:-
-regulate production of sperms.
-bring changes at puberty.
(ii) Vas deferns:
- It passes the sperm from the testes to the urethera.
(iii Urethera:-
- it is a common passage for both sperm and urine.
(iv) Associated gland:-
- Seminal vesicles and prostate gland add their secretion to the sperms. This fluid provides nourishment to sperms and make their transport easy.
- sperm along with secretion of glands form semen.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM:
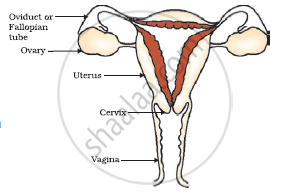
(i) Ovary
- A pair of ovary is located at both sides of the abdomen.
- Female germ cell i.e. eggs are produced here.
- At the time of birth of a girl, thousand of immature eggs are present in the ovary
- At the onset of puberty, some of these eggs start maturing.
- One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
(ii) Oviduct or Fallopian tube:-
- Receives the egg produced by the ovary and transfer it to the uterus.
- Fertilization i.e. fusion of gametes takes place here.
(iii) Uterus
- It is a bag like structure where development of the baby takes place
- uterus opens into vagina through cervix.
FERTILISATION OF EGG:-
- The fertilized egg called zygote is planted in uterus and develops into an embryo.
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mothers blood with the help of special tissue called placenta. It provides a large surface area for the exchange of glucose, oxygen and waste material.
- The time period from fertilization upto the birth of the baby is called gestation period.
WHEN EGG IS NOT FERTILISED:-
- The uterus prepares itself every month to receive fertilized egg
-The lining of the uterus becomes thick and spongy, required to support the embryo.
-When fertilisation had not taken place this lining is not needed any longer.
-This lining breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus.
-this cycle takes around 28 days every month and is called menstruation.
IMPLANTATION: In humans, implantation is the stage of pregnancy at which the embryo adheres to the wall of the uterus. At this stage of parental development, the conceptus is called a blastocyst. It is by this adhesion that the embryo receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother to be able to grow.
PLACENTA: The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. This structure provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby and removes waste products from the baby's blood. The placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus, and the baby's umbilical cord arises from it. The organ is usually attached to the top, side, front or back of the uterus. In rare cases, the placenta might attach in the lower uterine region (placenta previa).
GESTATION: Gestation, in mammals, the time between conception and birth, during which the embryo or fetus is developing in the uterus.
PARTURTION: The act or process of giving birth is known as parturtion.
